The accounting equation is the fundamental foundation of double-entry bookkeeping. It states that assets are equal to liabilities plus owners’ equity. This equation is the reason that debits must always equal credits in a well-kept set of books.
The equation is expressed as:
Assets = Liabilities + Owners’ Equity
What is the accounting equation?
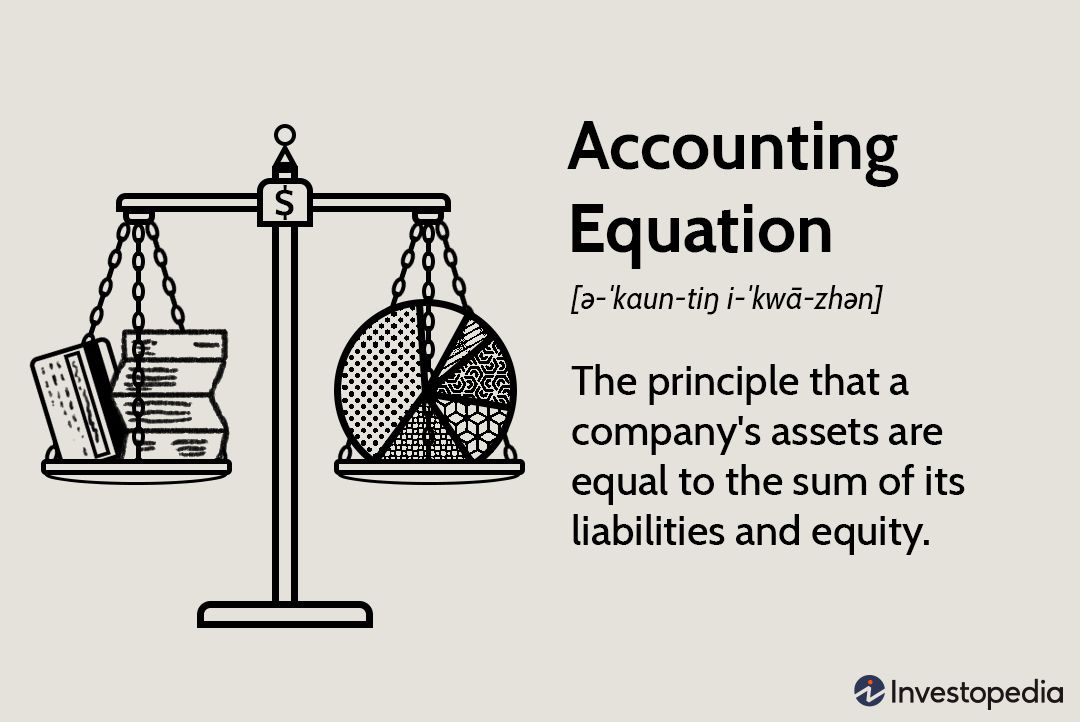
The accounting equation is the fundamental equation of double-entry accounting, which states that assets must always equal the sum of liabilities and equity. In other words, this equation ensures that a company’s books are always balanced.
This equation is represented as follows:
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
The left side of the equation (assets) represents all of the resources that a company owns and can use to generate income. The right side of the equation (liabilities and equity) represents all of the claims against those assets.
Liabilities are obligations that a company owes to others, such as creditors. Equity is the portion of ownership that remains after liabilities are paid off; it can be thought of as the residual claim on assets.
The accounting equation must always balance because, in theory, every transaction must have a dual effect on at least two different elements of the equation. For example, when a company issues shares of stock, this will increase equity while also increasing assets (since cash has been received). Conversely, when a company pays off a debt, this will decrease liabilities while also decreasing assets (since cash has been paid out).
What is income statement?

An income statement is one of the basic financial statements produced by a business. It shows how much revenue the business generated during a period of time, and how much expenses it incurred during that same period. The net income (or loss) for the period is calculated by subtracting the total expenses from the total revenue.
What is balance sheet?
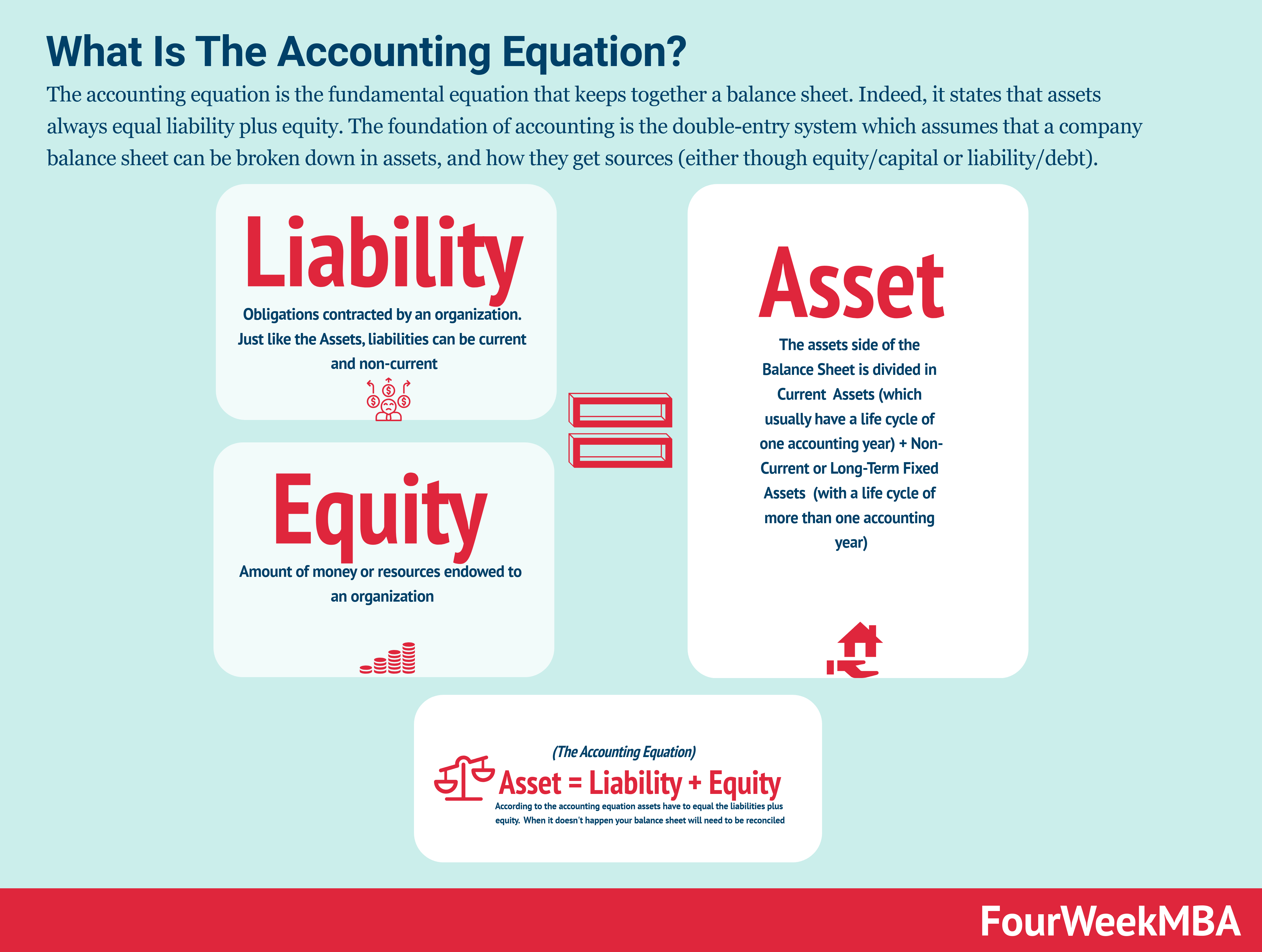
A balance sheet is a financial statement that reports a company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity at a specific point in time. The balance sheet is one of the three fundamental financial statements. These statements are key to both financial modeling and accounting.
The balance sheet equation is:
Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders’ Equity
This equation is the foundation for the balance sheet. The purpose of the balance sheet is to show a company’s financial position at a specific point in time. This financial position is composed of three elements: assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity.
Assets are everything that a company owns and can use to generate revenue. Liabilities are everything that a company owes to others. Shareholders’ equity is the residual claim that shareholders have on assets after liabilities have been paid.
The balance sheet equation must always be in balance. This means that if a company has more assets than liabilities, then shareholders’ equity must be positive. Similarly, if a company has more liabilities than assets, then shareholders’ equity will be negative. Finally, if assets and liabilities are equal, then shareholders’ equity will be zero.
How to use an accounting equation.
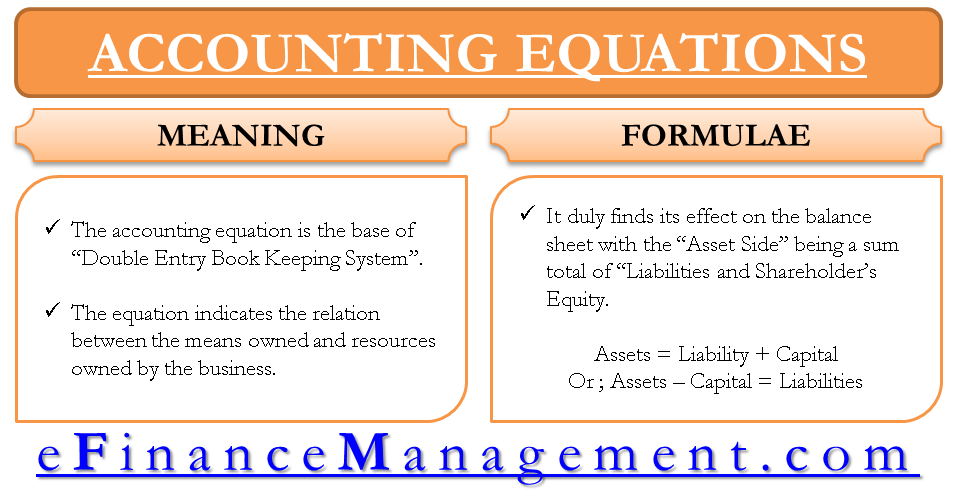
An accounting equation is a mathematical equation that represents the relationship between assets, liabilities, and owners’ equity in a business. This equation is the foundation of double-entry accounting, which is the method most businesses use to record financial transactions.
The accounting equation can be written as:
Assets = Liabilities + Owners’ Equity
This equation means that the total value of a business’s assets must always equal the sum of its liabilities and owners’ equity. In other words, assets are financed by either debt (liabilities) or investment by the owners (owners’ equity).
The accounting equation is also sometimes referred to as the balance sheet equation because it mirrors the way assets, liabilities, and owners’ equity are presented on a company’s balance sheet.
Tips for understanding an accounting equation.
In order to understand the accounting equation, it is important to first understand the basic concepts of assets, liabilities, and equity. Assets are items that are owned by the business and have value. Liabilities are debts or obligations that the business owes to others. Equity is the owner’s investment in the business.
The accounting equation states that assets must equal the sum of liabilities and equity. This means that if a business has more assets than liabilities, it has positive equity. If a business has more liabilities than assets, it has negative equity.
The accounting equation is important because it provides a framework for understanding a company’s financial position. By knowing what a company’s assets and liabilities are, we can better understand its financial health and make informed decisions about investing in or lending to the company.
What Is Accounting Equation? – Accounting Equation Financial Definition
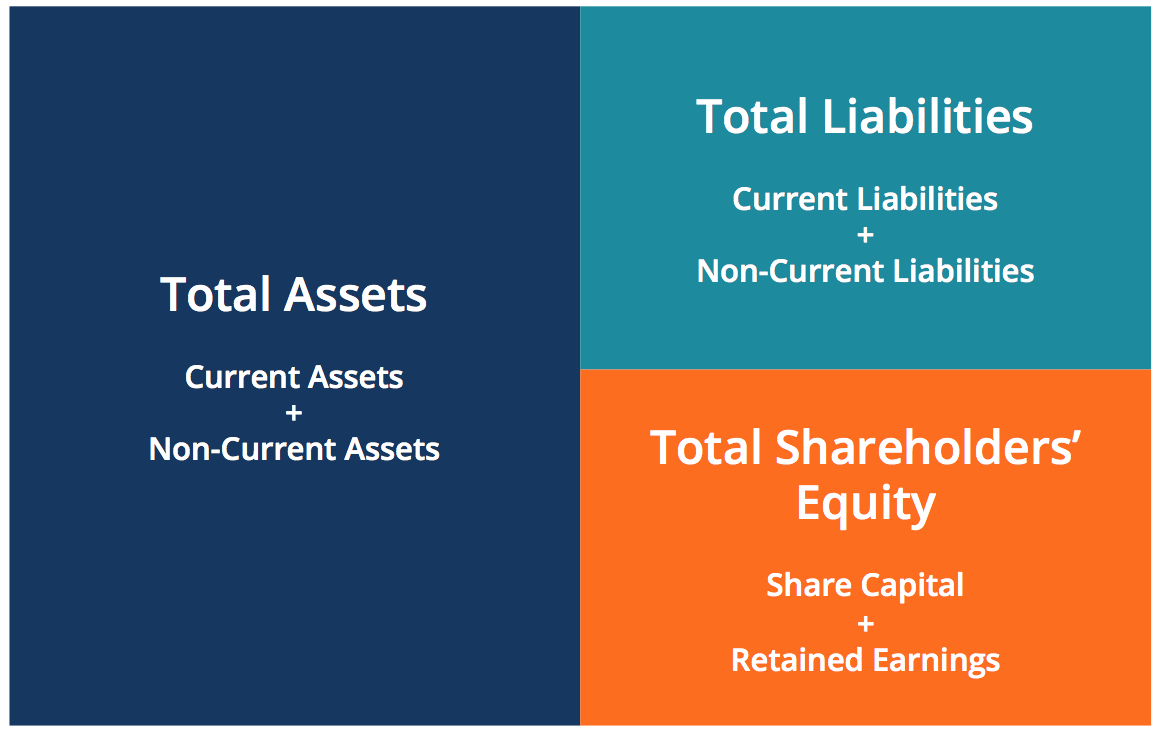
In the most basic terms, the accounting equation is the relationship between a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity. This equation is the foundation of double-entry bookkeeping, which is used by most businesses today.
The accounting equation can be expressed as follows:
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
This equation must always balance – that is, the left side must always equal the right side. This is because a company’s total assets must always equal the sum of its liabilities and equity. Let’s take a closer look at each side of the accounting equation.
Assets are everything a company owns that has monetary value. This includes cash, accounts receivable (money owed to the company by customers), inventory, equipment, buildings, and vehicles. In short, anything that a company uses to generate revenue is an asset.
Liabilities are everything a company owes to others. This includes accounts payable (money owed to suppliers), loans, and credit card balances. Basically, any money that a company owes to someone else is considered a liability.
Equity is the difference between a company’s assets and liabilities – in other words, it’s what a company owns after liabilities are subtracted from assets. For example, if a company has total assets of $100,000 and total liabilities of $50,000, then its equity would be $50,000 ($100,000 – $50,000).