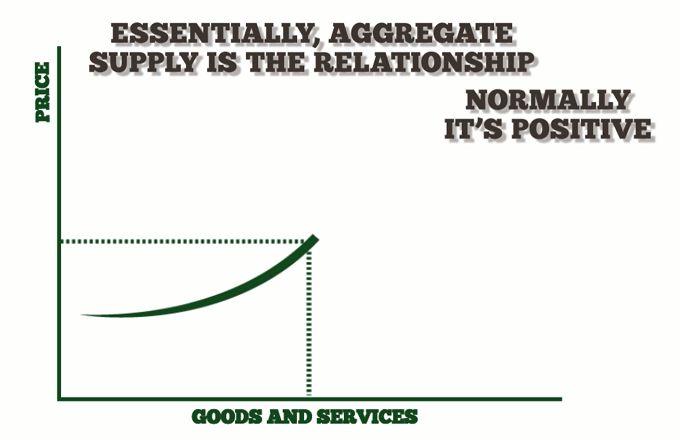
Aggregate supply is an important concept in economics and finance that refers to the total amount of goods and services that businesses are willing to offer in a given market. It is a key component in the determination of a nation’s gross domestic product (GDP) and is closely linked to the demand for goods and services. Understanding the concept of aggregate supply is essential for businesses to make informed decisions about how to allocate resources and maximize profits. This article will discuss the definition of aggregate supply, how it affects economic growth, and the factors that influence it.
What Is Aggregate Supply and How Does It Impact the Economy?
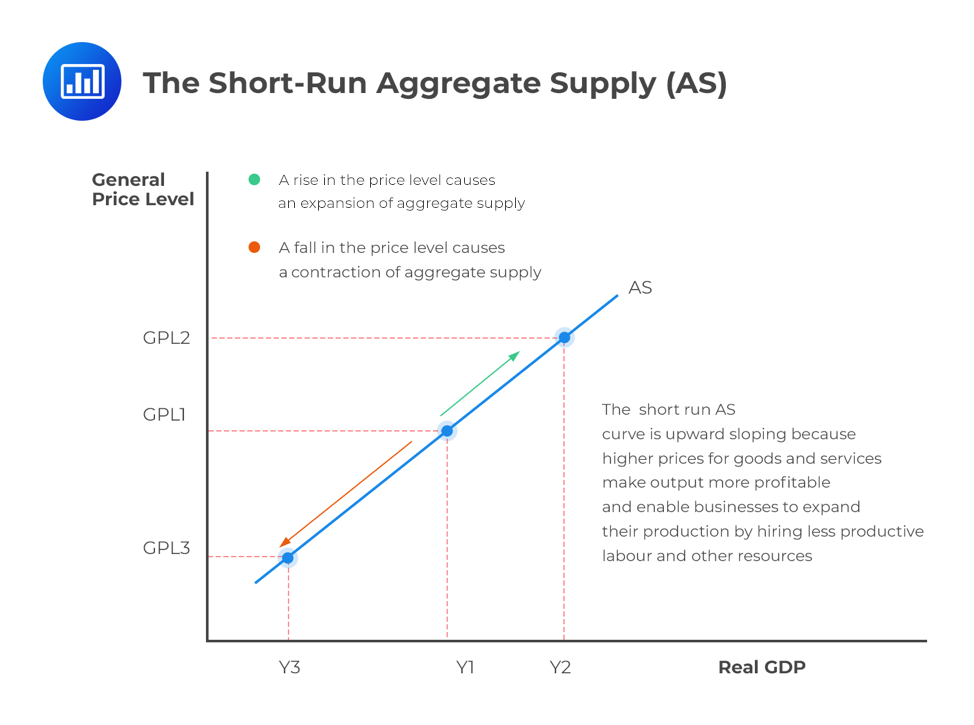
Aggregate supply is an important concept in economics which refers to the total amount of goods and services that businesses and producers in an economy are willing and able to produce. It is an important measure of economic activity and is an important component in understanding how an economy works. Aggregate supply measures the total output of an economy, which is then used to calculate GDP and other economic metrics. Aggregate supply has a significant impact on the economy, as it can influence prices, employment, and economic growth. When aggregate supply is high, prices tend to be low and businesses are more likely to hire more workers, which can lead to economic growth. When aggregate supply is low, prices tend to be higher and businesses are less likely to hire more workers, which can lead to economic contraction. By understanding aggregate supply and its impact on the economy, it can help economists and policy makers to make informed decisions about economic policies and help to ensure economic stability.
Identifying the Three Components of Aggregate Supply
Aggregate supply is a macroeconomic concept that refers to the total amount of goods and services produced by an economy at a given overall price level in a given period of time. It is made up of three components: potential output, cyclical fluctuations, and changes in prices. Potential output is the maximum amount of goods and services an economy can produce under full employment. Cyclical fluctuations refer to changes in the amount of goods and services produced due to economic factors such as consumer spending and business investment. Changes in prices, on the other hand, refer to the effect of inflation or deflation on the price of goods and services. Understanding how these three components of aggregate supply interact with each other can help economists better understand how an economy is performing and how to create policies that will lead to economic growth.
Examining the Impact of Government Policies on Aggregate Supply
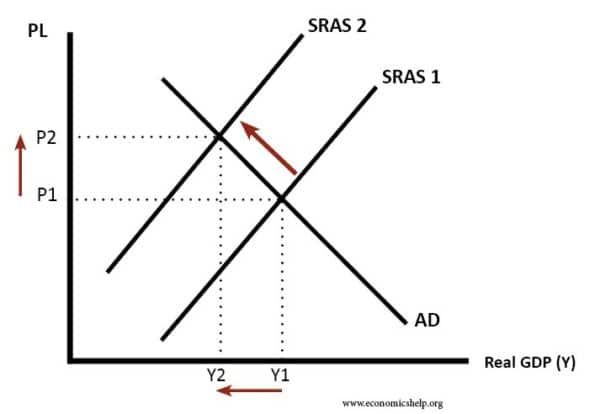
Government policies have a huge impact on aggregate supply, which is the total amount of goods and services that businesses in an economy are willing and able to produce within a certain time period. The aggregate supply curve shows the relationship between the price level of the goods and services and the quantity supplied. Government policies such as taxation, spending, and inflation have the power to change the curve and the resulting price level and quantity of goods and services. For example, if the government increases taxes, businesses may reduce their production and prices could increase. On the other hand, if the government lowers taxes or increases spending, businesses may increase their production and prices could decrease. It’s important to understand how government policies affect aggregate supply in order to predict how the economy will react to changes in policy.
Analyzing the Impact of Global Factors on Aggregate Supply
Global factors have a huge impact on aggregate supply, and it’s important to understand how they affect the overall economy. As the global economy becomes more interconnected, the actions of one country can reverberate across the world. For instance, a policy change in one country can affect the cost of goods, the availability of capital, and the level of economic activity in other countries. This, in turn, can affect the overall aggregate supply in an economy. It’s also important to consider how changes in the global financial system can affect aggregate supply. For instance, changes in currency exchange rates or interest rates can affect the cost of goods and the availability of capital, which can have a ripple effect on aggregate supply. It’s also important to consider how the global political environment can affect aggregate supply, as changes in government policies or regulations can have a direct impact on production and the cost of goods. Understanding how global factors can impact aggregate supply is essential for making informed economic decisions.
Exploring the Relationship Between Aggregate Supply and Demand

Exploring the relationship between aggregate supply and demand can be a complex concept. Aggregate supply is the total amount of goods and services that businesses in an economy are willing and able to provide at a given price level in a given period of time. On the other hand, aggregate demand is the total amount of goods and services that consumers are willing and able to purchase in an economy at a given price level in a given period of time. The relationship between aggregate supply and demand is important to understand in order to get an idea of the overall economic health of a country. When aggregate supply and demand are in balance, it indicates a healthy and stable economy, while an imbalance can be a sign of economic trouble. The relationship between aggregate supply and demand is a crucial factor to consider when analyzing economic trends and making decisions about economic policies.