In accounting, the accruals principle is the concept of recording revenues and expenses when they are earned or incurred, regardless of when the cash is actually received or paid.
The accruals principle is important because it provides a more accurate picture of a company’s financial position than would be the case if transactions were only recorded when cash changed hands.
For example, if a company sells goods on credit, the sale should be recorded as revenue when the goods are delivered, even though the cash may not be received until some later date.
What is Accruals?
An accrual is an accounting term that refers to the recognition of revenue and expenses that have been incurred, but have not yet been paid or recorded. Accruals are recorded in the accrual method of accounting, which is a system of recording financial transactions that recognizes revenue and expenses when they are earned or incurred, regardless of when the payment is actually received or made.
The accrual method of accounting is used by most businesses, as it provides a more accurate picture of a company’s financial position than the cash basis method of accounting, which only recognizes transactions when cash is exchanged.
Accruals are important because they allow businesses to track and report their revenue and expenses in a more timely and accurate manner. Without accruals, businesses would only be able to report their financial position at the end of each year, which would make it difficult to manage their finances on a day-to-day basis.
How Does Accrual Accounting Work?
In accrual accounting, revenues and expenses are recognized when they are earned or incurred, regardless of when the cash is received or paid. For example, if a company provides a service to a customer in December but doesn’t bill the customer until January, the revenue would still be recognized in December. This matching of revenues and expenses is intended to give a more accurate picture of a company’s financial position than cash-basis accounting, which only recognizes transactions when cash changes hands.
Accrual accounting is generally used by businesses and other organizations, but it can also be used by individuals. For example, if you mow your neighbor’s lawn in June but don’t charge them until July, you could use accrual accounting to record the revenue in June and the expense (of gas and your time) in July.
When Do You Use Accruals and When do you use Cash Methods?

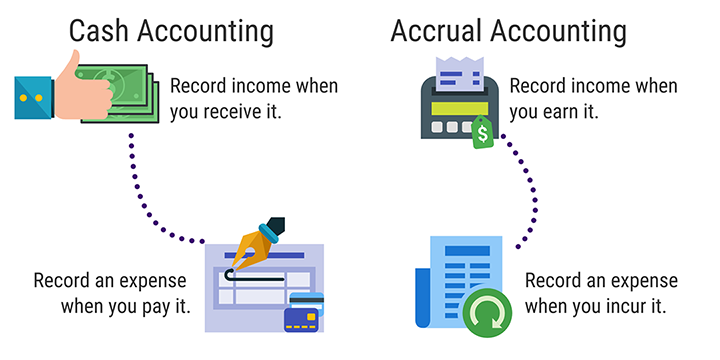
There are two types of accounting methods used to record and report business transactions: accrual accounting and cash accounting.
Accrual accounting records transactions when they occur, regardless of when money is exchanged. This method provides a more accurate picture of a company’s financial position because it shows all the company’s assets and liabilities.
Cash accounting records transactions only when money is exchanged. This method is simpler and easier to understand, but it can provide a misleading picture of a company’s financial position because it does not show all the company’s assets and liabilities.
So, which accounting method should you use? It depends on your business and what type of information you need.
Why Do Companies Prefer Accrual Accounting?
There are a few key reasons that businesses prefer to use accrual accounting rather than cash accounting. The main advantages of accrual accounting are that it provides a more accurate picture of a company’s financial position and it better matches income and expenses to the period in which they were actually incurred.
Accrual accounting also makes it easier to compare financial results from one period to another. This is because all income and expenses are recorded in the period in which they occur, regardless of when the money is actually received or paid. This provides a more accurate picture of a company’s financial performance over time.
How Does the Balance Sheet Impact a Company’s Financial Report through Accruals Reporting?
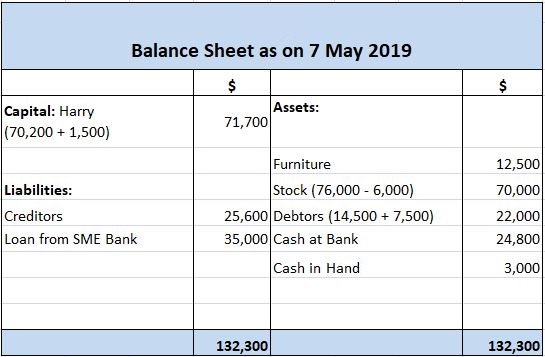
The balance sheet, also known as the statement of financial position, is a report that summarizes a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. The balance sheet is one of the three primary financial statements used by businesses, along with the income statement and cash flow statement.
The balance sheet impacts a company’s financial report through accruals reporting. Accruals are items that are earned or incurred but have not yet been paid for or collected. For example, if a company provides services to a customer but does not receive payment until the following month, the revenue would be reported as an accrual on the balance sheet.
Accruals are important because they provide a more accurate picture of a company’s financial position. By including accruals, businesses can better manage their cash flow and make more informed decisions about spending and investment.
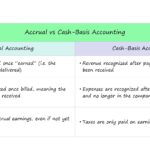
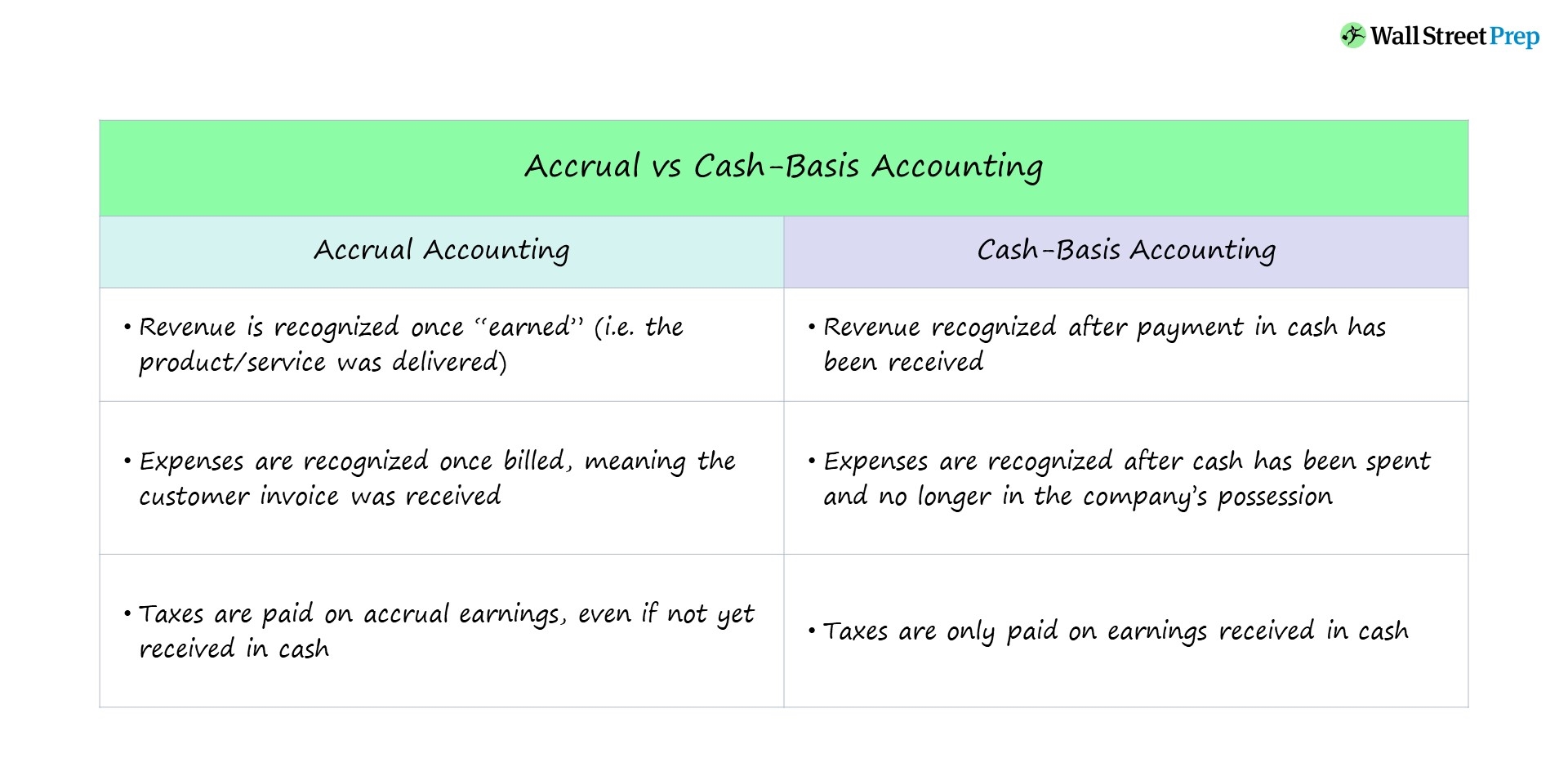
What Is Accruals? – Accruals Financial Definition
Accruals are items that have been earned or incurred but not yet paid or recorded. In accrual-based accounting, expenses and revenues are recognized when they are earned or incurred, regardless of when the cash is actually paid out or received. This approach provides a more accurate picture of a company’s financial position than cash-based accounting, which recognizes only items when the cash is paid or received.
The accruals concept is important in understanding the timing of recognition for revenues and expenses. For instance, if a company provides a service on credit, the revenue from that service is not recognized until the customer pays the bill. Similarly, if a company incurs an expense but does not pay for it immediately, the expense is not recognized until it is paid.
While the accruals concept is essential to understanding financial statements, it can also be confusing. The following example illustrates how accruals can impact the timing of recognition for expenses and revenues.
Suppose ABC Company provides consulting services on credit. ABC records revenue when the services are performed, regardless of when the customer pays the bill. Assume ABC performs $1,000 of consulting services in January and sends invoices to its customers in January. Customer A pays its invoice in February, while customer B does not pay until March. In this case, ABC would recognize $1,000 of revenue in January (when the services were performed), even though it would not receive any cash until February or