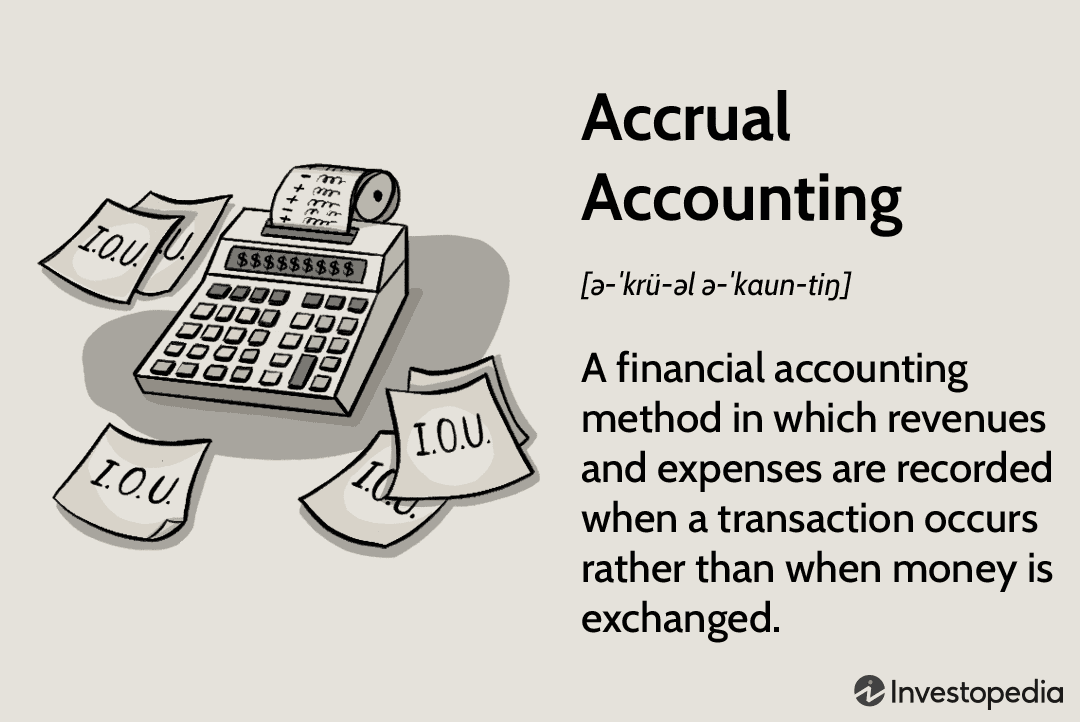
If you’re running a business, or even just handling your personal finances, you’ve probably heard of accrual accounting. But what is it, exactly?
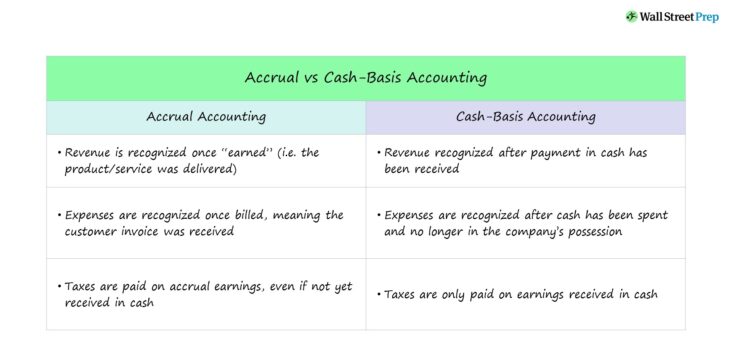
Accrual accounting is an accounting method that recognizes economic events regardless of when cash is exchanged. In other words, revenue is recognized when earned, rather than when the money is actually received. This method provides a more accurate picture of a company’s financial position than cash accounting, which only recognizes transactions when cash changes hands.
While accrual accounting is generally more accurate than cash accounting, it can also be more complicated. In this blog post, we will explore the basics of accrual accounting and how it works.
What Is Accrual Accounting?
In accrual accounting, revenue is recognized when earned, not when received. Similarly, expenses are recognized when incurred, not when paid. The goal of accrual accounting is to match revenue and expenses in the period in which they are incurred. This provides a more accurate picture of a company’s financial performance than cash basis accounting, which only recognizes revenue and expenses when cash is exchanged.
There are several key benefits to using accrual accounting. First, it provides a more accurate picture of a company’s financial performance. This is because accrual accounting matches revenue and expenses in the period in which they are incurred, rather than when cash is exchanged. This gives management a better idea of how the business is performing on a month-to-month or year-to-year basis.
Second, accrual accounting is easier to use for tax purposes. This is because tax laws typically require businesses to use accrual accounting when calculating their taxes. Finally, accrual accounting gives creditors and investors a better idea of a company’s future financial prospects. This is because it provides information on expected future cash inflows and outflows.
How Accrual Accounting Is Different From Cash or Cost Accounting

Accrual accounting is different from cash or cost accounting in several key ways. First, accrual accounting recognizes revenue when it is earned, not when it is collected. This means that revenue can be recognized even if the money has not yet been received. Second, accrual accounting matches expenses to the period in which they are incurred, rather than when they are paid. This provides a more accurate picture of a company’s financial health. Finally, accrual accounting requires the use of accrual journals and ledgers to record transactions.
When Should You Use Accrual Accounting?
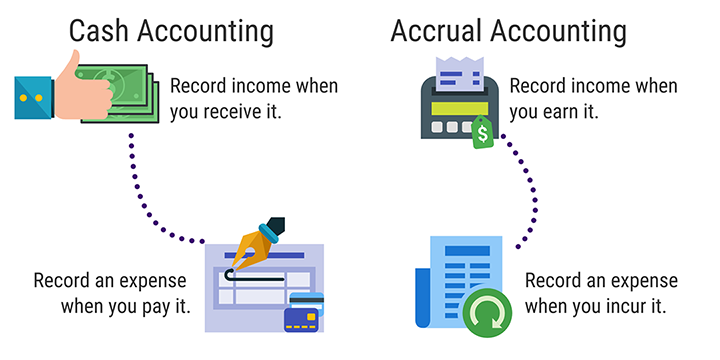
In accrual accounting, transactions are recorded when they occur, regardless of when the cash is received or paid. This method provides a more accurate picture of a company’s financial position at any given time.
There are a few key times when you should use accrual accounting:
1. When you need to track inventory levels and costs – Accrual accounting can give you a more accurate picture of your inventory levels and associated costs. This information is important for making strategic decisions about purchasing and pricing.
2. When you need to know the true cost of goods sold – If you want to get an accurate picture of your company’s profitability, you need to know the true cost of goods sold. Accrual accounting can help you track these costs more accurately.
3. When you need to manage accounts receivable and accounts payable – Accrual accounting can give you a better understanding of your company’s accounts receivable and accounts payable. This information can be helpful in managing cash flow and making decisions about credit terms.
Why You Should Still Consider Cash or Cost Accounting
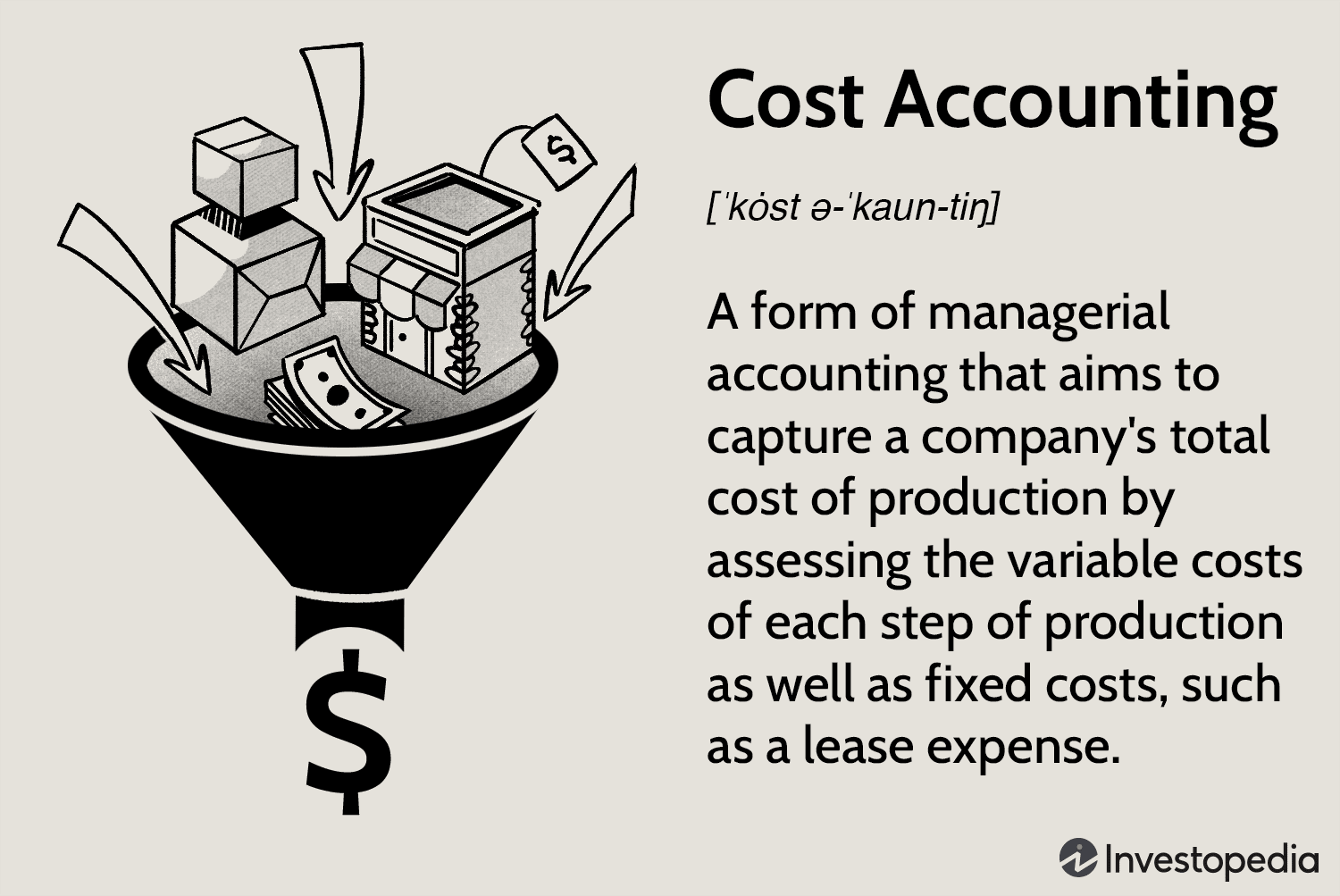
While accrual accounting is the standard for financial reporting, there are still some instances where cash or cost accounting may be more appropriate.
If you’re a small business owner, you may be more familiar with cash accounting, which records transactions when money changes hands. This method can be simpler to track and understand than accrual accounting.
Cost accounting may also be a good option if your business produces products rather than services. This method focuses on the cost of goods sold, rather than revenue earned.
Ultimately, the best accounting method for your business depends on your specific needs and goals. If you’re not sure which approach is right for you, talk to a certified public accountant or other financial advisor.
What Is Accrual Accounting? – Accrual Accounting Financial Definition

Accrual accounting is an accounting method that recognizes economic events regardless of when cash is exchanged. In other words, revenue is recognized when earned, rather than when the cash is received, and expenses are recognized when incurred, rather than when the cash is paid out.
The accrual basis of accounting is generally thought to provide a more accurate picture of a company’s financial position and results of operations than does the cash basis of accounting. The main advantage of accrual accounting is that it matches revenues with expenses, so that you can get a better sense of how profitable your business is.
There are some disadvantages to using accrual accounting, however. First, it can be more complicated than cash basis accounting, since you have to track both receivables and payables. Second, it may not give you as much of a Cash Flow as you would like, since revenue may be recognized before cash is actually received.