Understanding the concept of After-Tax Real Rate of Return (ARR) is essential for any investor looking to maximize their returns while minimizing their tax burden. ARR provides a more accurate picture of an investment’s performance, taking into account any taxes owed on returns and adjusting for inflation. By analyzing ARR, investors can make more informed decisions on where to place their money, ensuring they are getting the most return on their investment. In this article, we will discuss what After-Tax Real Rate of Return is, how to calculate it and how to use it in your investing strategy.
What is After-Tax Real Rate of Return?
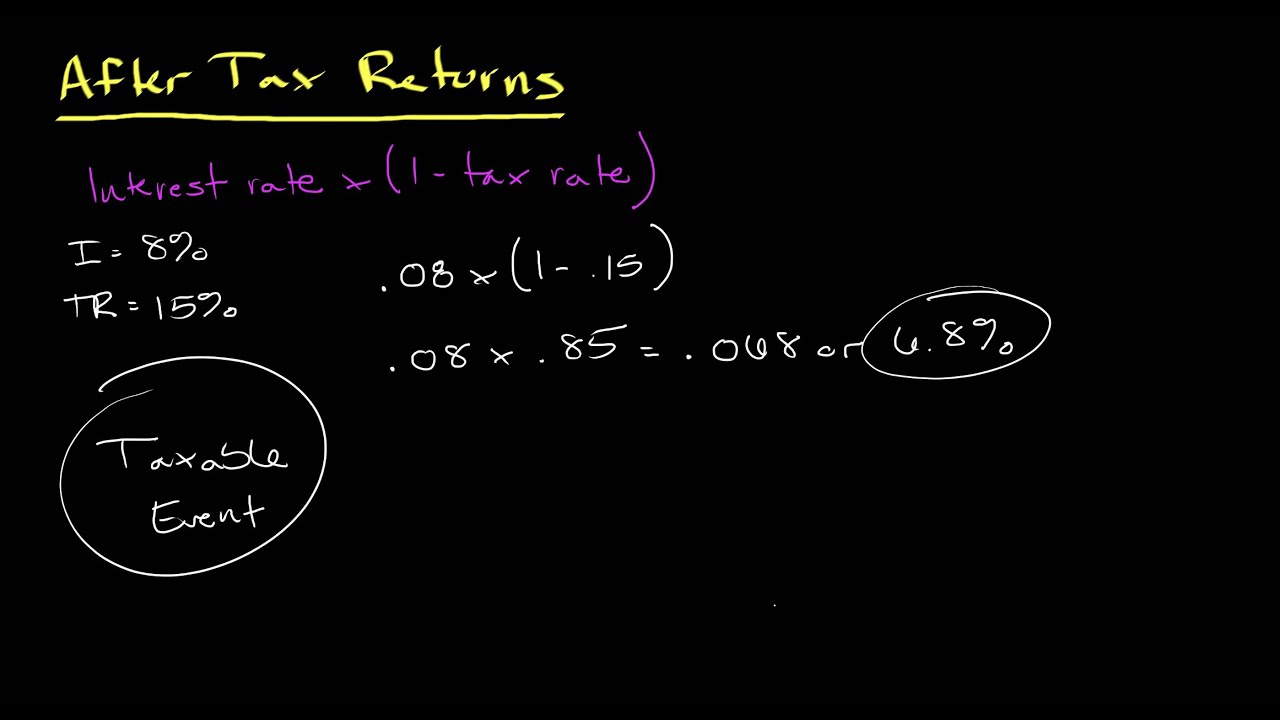
After-Tax Real Rate of Return is an important financial concept that all investors should understand. It is the rate of return that investors make on their investments after taking into account taxes, inflation, and other costs. This rate of return is calculated by subtracting the rate of inflation from the rate of return on an investment, then subtracting taxes from the resulting number. The result is the After-Tax Real Rate of Return. It is important to remember that this rate of return is not the same as the nominal rate of return, which does not take into account taxes and inflation. The After-Tax Real Rate of Return can give investors a better idea of how much money they are actually making on their investments, as opposed to just looking at the nominal rate of return. Knowing this rate of return can help investors make more informed decisions when investing their money.
Calculating After-Tax Real Rate of Return

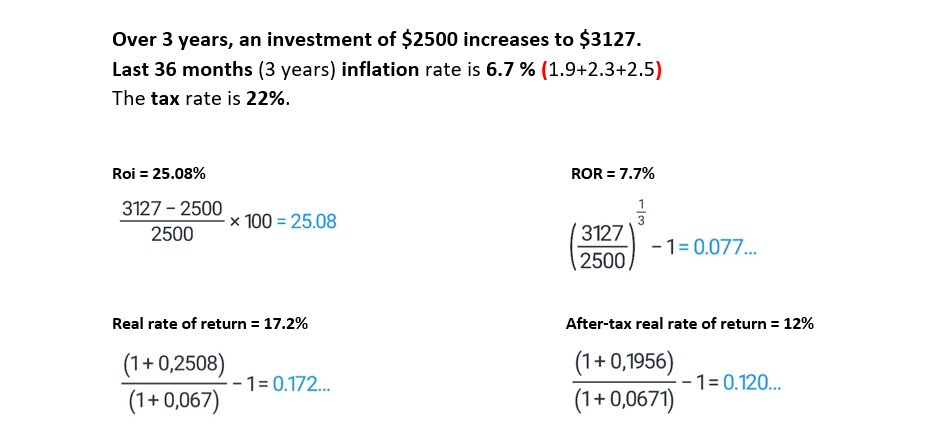
Calculating after-tax real rate of return is essential for assessing the true value of investments. Many investors make decisions based on the pre-tax rate of return, but this does not take into account the effects of taxes, which can significantly reduce the amount of money you make on an investment. To calculate your after-tax real rate of return, you need to know the expected return of your investment, the rate of tax you will be subject to, and the inflation rate. Subtract the rate of tax from the expected return to get the pre-tax rate of return. Then subtract the inflation rate from the pre-tax rate of return to get the after-tax real rate of return. This figure is the true rate of return on your investment, taking into account the effects of taxes and inflation.
Benefits of Knowing Your After-Tax Real Rate of Return

Knowing your after-tax real rate of return is a great way to make sure you’re getting the most out of your investments. By understanding your rate of return after taxes, you can ensure that your investments are working for you and giving you the best return possible. The after-tax real rate of return takes into account any taxes that you might have to pay on your gains, giving you a more accurate picture of your true rate of return. This can be especially useful if you’re investing in risky investments, as you’ll have a better understanding of the potential return you can expect after taxes. Knowing your after-tax real rate of return is a great way to make sure you’re getting the most out of your investments and can help you make smarter decisions when it comes to investing.
Strategies for Increasing Your After-Tax Real Rate of Return
If you want to maximize your after-tax real rate of return, there are a few strategies you can implement. One of the most effective strategies is to invest in assets that are tax-advantaged. This includes investments in retirement accounts like IRAs and 401(k)s, which allow your money to grow tax-free until you start making withdrawals. Another strategy is to invest in stocks and bonds that are tax-exempt, such as municipal bonds. This means that you won’t have to pay taxes on the interest you receive. Finally, you can take advantage of tax credits and deductions to reduce your taxable income. By utilizing these strategies, you can maximize your after-tax real rate of return and enjoy more of your hard-earned money.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Calculating After-Tax Real Rate of Return

When it comes to calculating your after-tax real rate of return, there are a few common mistakes you should avoid. Firstly, it’s important to remember that you need to take into account any inflation that may occur. If you don’t adjust your rate of return for inflation, you could end up with a much lower return than expected. Additionally, you should also consider any taxes that may be due on the investment, as this can have a significant impact on your real rate of return. Finally, make sure to take into account any fees and commissions associated with the investment, as these can further reduce your real rate of return. By avoiding these common mistakes, you can ensure that you are getting the most out of your investments.