Discover the secrets to making money in the stock market with our comprehensive guide, designed to help you unlock the true potential of your investments. Tap into expert strategies, tips, and insights to maximize your profits and minimize risks, all while navigating the exciting world of stocks and shares. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out, our proven techniques will empower you to seize lucrative opportunities and achieve financial success. Don’t miss your chance to turn your stock market dreams into reality – dive into our wealth of knowledge and start multiplying your money today!
Long-term investing: One of the most common ways to make money in the stock market is through long-term investing

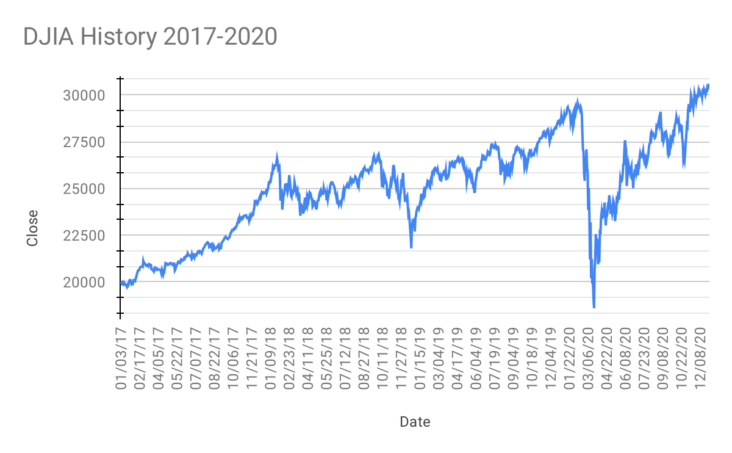
Long-term investing is a popular and reliable method to generate wealth in the stock market. By focusing on stable, high-quality stocks with a proven track record of success, investors can capitalize on the power of compounding returns and minimize risks associated with market volatility. This strategy requires patience, discipline, and a keen eye for identifying companies with strong fundamentals, competitive advantages, and potential for growth. By consistently investing in these stocks over an extended period, investors can maximize their returns and achieve financial success. Adopting a long-term investing mindset is crucial for building a robust and diverse portfolio that stands the test of time.
This involves buying stocks and holding onto them for an extended period, often years or even decades

Investing in stocks for the long-term is a proven strategy to build wealth and generate passive income. This method, known as buy-and-hold investing, involves purchasing stocks in stable, well-established companies and holding onto them for an extended period, often spanning years or even decades. By choosing companies with strong fundamentals, impressive track records, and a history of consistent growth, investors can ride out market fluctuations and capitalize on the power of compounding. Patience and discipline are key when employing this strategy, as it allows your investments to grow over time, resulting in potentially significant returns and financial freedom.
This strategy is based on the idea that, over time, the stock market tends to increase in value, and that individual companies will grow and become more profitable

The long-term investment strategy, built on the premise that the stock market generally appreciates in value over time, is a proven approach for generating wealth through stocks. By selecting well-established, financially stable companies with a history of consistent growth, investors can capitalize on the continual expansion and increased profitability of these businesses. Patience and a well-diversified portfolio are essential components of this strategy, ensuring that you mitigate risks while maximizing returns. By consistently investing and taking advantage of compounding interest, the long-term investor can enjoy substantial financial gains in the ever-evolving stock market.
By holding onto stocks for the long term, investors can benefit from both capital appreciation (the increase in the stock price) and dividend payments (regular payouts from the company’s profits).
By adopting a long-term investment strategy, individuals can optimize their financial gains in the stock market through capital appreciation and dividend payments. Capital appreciation occurs when the value of a stock increases over time, potentially yielding significant returns for patient investors. Additionally, many companies reward their shareholders with regular dividend payouts, which are derived from the organization’s profits. By holding onto stocks for an extended period, investors can benefit from these dual income streams, leading to a more fruitful and secure financial future. In essence, a long-term approach in stock market investing can create a strategically sustainable and lucrative portfolio for those willing to exercise patience and diligence.
Dividend investing: Dividend investing focuses on purchasing stocks of companies that pay out regular dividends, which are a portion of the company’s earnings distributed to shareholders

Dividend investing is a strategic approach to building wealth in the stock market by targeting companies known for their consistent dividend payouts. By carefully selecting stocks with a strong history of dividend payments, investors can enjoy passive income streams while also benefiting from potential capital appreciation. This long-term investment strategy not only helps in diversifying your portfolio but also provides a hedge against market volatility. As a result, dividend investing is ideal for those who seek financial stability and steady returns. By reinvesting these dividends into more shares, investors can further amplify their gains and accelerate the compounding effect, leading to exponential growth in their investments.
By investing in dividend
Investing in dividend-paying stocks is a proven strategy for generating income in the stock market. By focusing on companies with solid financials and a history of consistently paying dividends, you can potentially benefit from a steady stream of passive income. Dividend investing not only offers the opportunity for regular cash payouts but also the chance for potential capital appreciation as stock prices increase over time. To maximize your returns in this investment approach, it’s essential to diversify your portfolio and reinvest the dividends into additional shares, allowing for compound growth. By being patient and maintaining a long-term view, dividend investing can be a powerful tool for wealth creation.