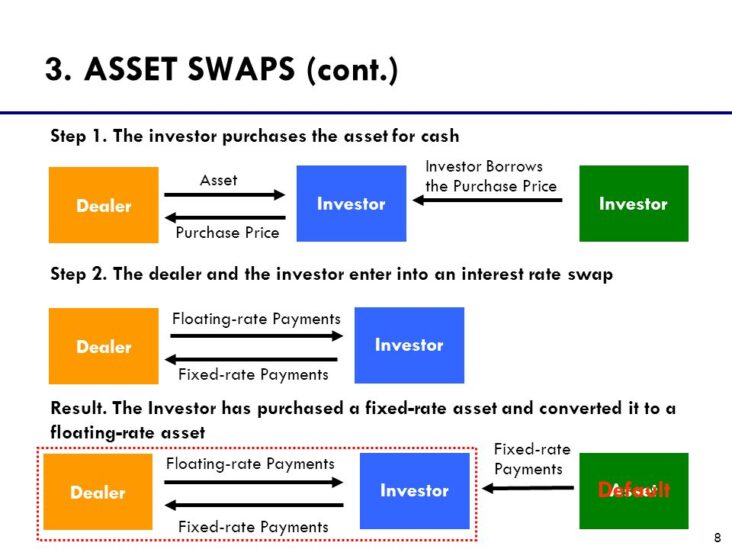
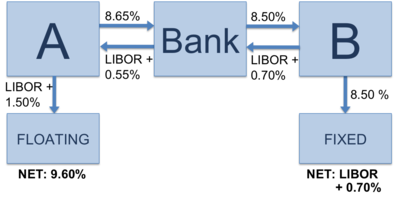
Asset swaps are an increasingly popular financial tool used by investors to realize higher returns from their investments. An asset swap is a type of transaction whereby two parties exchange two different assets, usually an income-generating asset for another asset, with the goal of achieving higher yields and greater returns. Asset swaps can involve anything from bonds, equities, and derivatives to currencies or commodities and can be used for both hedging and speculation. By understanding the basics of asset swaps, investors can take advantage of this powerful tool to increase their returns and manage their portfolios more effectively.
What Is an Asset Swap and How Does it Work?
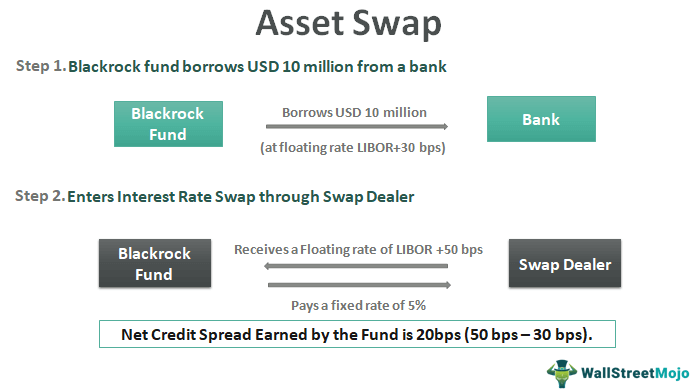
An asset swap is a financial transaction where two parties agree to exchange different types of assets. It’s a way to diversify your portfolio, or to make an investment at a lower cost. The two parties agree to exchange one asset for another, usually at a predetermined rate. This can be done in a variety of ways, and the type of asset swapped can vary too. For example, one party might offer a bond, while the other might offer a stock. The exchange rate is based on the market value of the assets, and the two parties can negotiate a price that meets their needs. Asset swaps are a great way to unlock the value of your investment portfolio, and can be used to increase returns or to lower the cost of investment.
Benefits and Risks of Asset Swaps
Asset swaps offer a unique way to benefit from potential gains while also minimizing the potential risks. Asset swaps can provide a great way to diversify your portfolio and increase returns. By swapping a less risky asset for a more risky one, you can reduce the risk of a single asset and spread out the potential rewards and losses. The potential rewards can come from the appreciation of the less-risky asset, while the potential losses can come from the depreciation of the more risky asset. However, asset swaps come with their own risks as well. The biggest risk to consider is the counterparty risk. This is the risk that the other party involved in the swap will not honor the agreement. This could lead to a financial loss. Additionally, the value of the asset can change drastically between the time of the agreement and the time of the swap, leaving one side with a loss and the other with a gain. It is important to be aware of these risks when considering an asset swap.
The Different Types of Asset Swaps

Asset swaps are great for investors looking for more creative and flexible ways to invest their money. There are many different types of asset swaps, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Interest rate swaps are the most common type of asset swap, where two parties agree to exchange cash flows, usually based on a floating rate of interest, in order to reduce their interest rate risk. Credit default swaps are another type of asset swap that allow investors to protect their investments from default, by buying protection from a third party in exchange for a fee. Equity swaps are a type of asset swap that allows investors to exchange equity-based cash flows, such as dividends and stock prices, with fixed rate payments. Currency swaps are a type of asset swap that allow investors to exchange one currency for another, in order to reduce currency risk. Commodity swaps are a type of asset swap that allow investors to exchange commodities, such as oil, gold, and agricultural products, for fixed rate payments. Asset swaps provide investors with flexibility and creativity when it comes to investing, and can be beneficial depending on the investor’s goals and risk tolerance.
The Process of Completing an Asset Swap
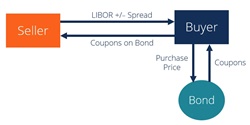
An asset swap is a financial transaction in which two parties exchange assets to achieve their respective investment goals. The process of completing an asset swap involves evaluating the risks and benefits of the swap, negotiating a price, and executing the swap itself. It’s important to consider the liquidity of the assets, the creditworthiness of the counterparties, and the legal and tax implications of the swap. When done correctly, an asset swap can be a great way to get the most out of your investments. It’s important to do your research and understand the process before entering into an asset swap. If you have any questions or concerns, it’s best to consult a professional financial advisor. Taking the time to understand the process and the risks associated with it can help ensure a successful asset swap.
When Is an Asset Swap the Right Financial Move?
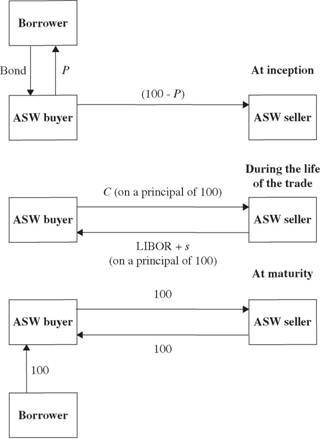
If you’re looking for the right financial move, an asset swap might be the answer. An asset swap is when two parties agree to exchange one asset for another. It’s a great way to diversify your portfolio, increase return on investments, and reduce risk. Asset swaps can also be used to hedge against potential losses. Asset swaps are often used in situations where there is a need to exchange debt securities, such as bonds, for equity, such as stocks. Asset swaps can be tailored to suit individual needs and provide flexible financial solutions. With the right financial move, an asset swap can create significant value for both parties involved.