Have you ever heard of an amortized bond? In this article, we will explain what an amortized bond is, how it works, and the advantages and disadvantages of investing in one. An amortized bond is a type of debt instrument that pays periodic interest payments over the life of the bond and repays the principal at maturity. It is an attractive investment for those looking for a steady income stream and a predictable return on their investment. We will cover how amortized bonds are used, how they are different from other bonds, and the advantages and disadvantages of investing in them. With this information, you will be better informed to make your own investment decisions.
What Does Amortized Bond Mean?
An amortized bond is a type of debt instrument that is structured to be paid back in regular installments over a predetermined period of time. This type of bond is typically offered by corporations and other entities to investors who are seeking to earn a fixed rate of return on their investment. The payments made to the investors are calculated based on the amortization schedule of the bond, which outlines the payment amount and due date for each payment. Amortized bonds are typically issued with a fixed interest rate and a fixed maturity date, and they provide a reliable and steady stream of income to investors. These bonds can be a great way to diversify your portfolio, as they are generally considered to be low-risk investments.
What Are the Benefits of an Amortized Bond?
Having an amortized bond can be a great benefit for anyone looking to invest. An amortized bond is a bond where the face value of the bond is paid back to the investor over a certain period of time. This allows the investor to receive a steady stream of income instead of just a one-time lump sum. This is great for people who don’t have the means to invest large amounts of money all at once, or for those who want to spread out their returns over a long period of time. Additionally, amortized bonds are typically lower-risk investments since the payments are usually backed by the issuer’s assets. This means that the investor is less likely to see a large loss in the event that the issuer defaults on the loan.
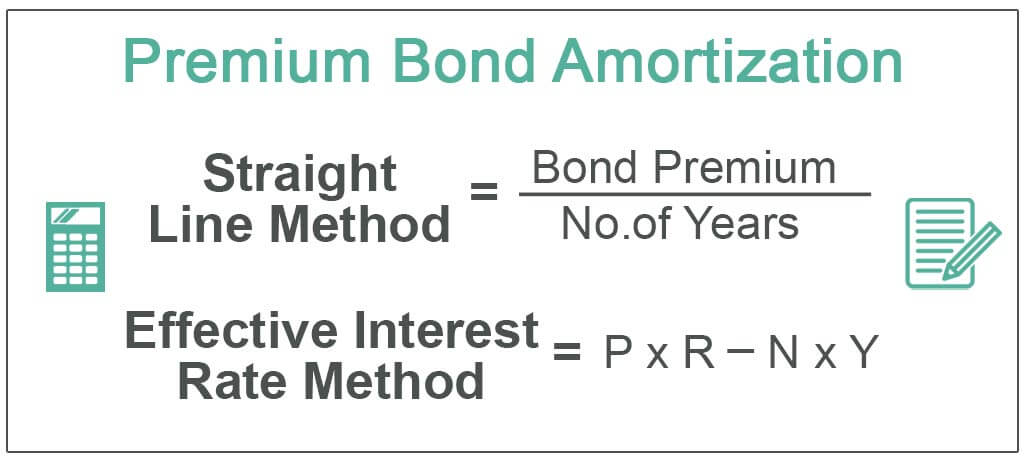
How to Calculate the Amortized Bond Value?
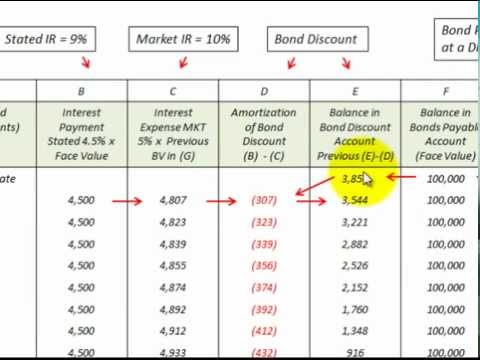
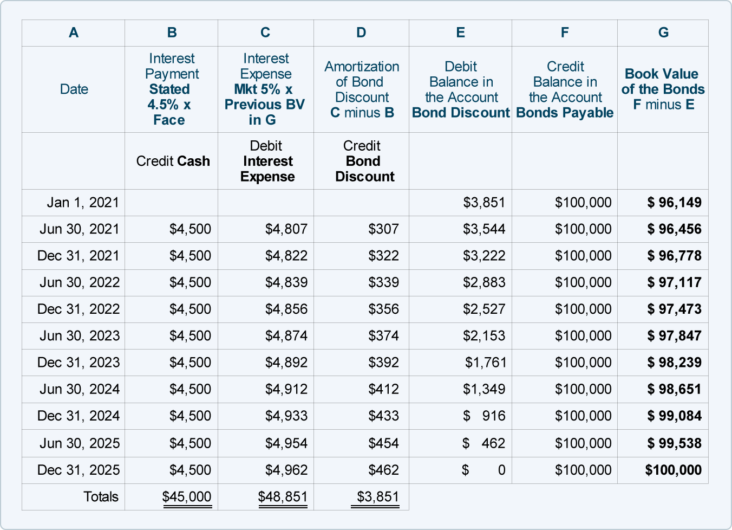
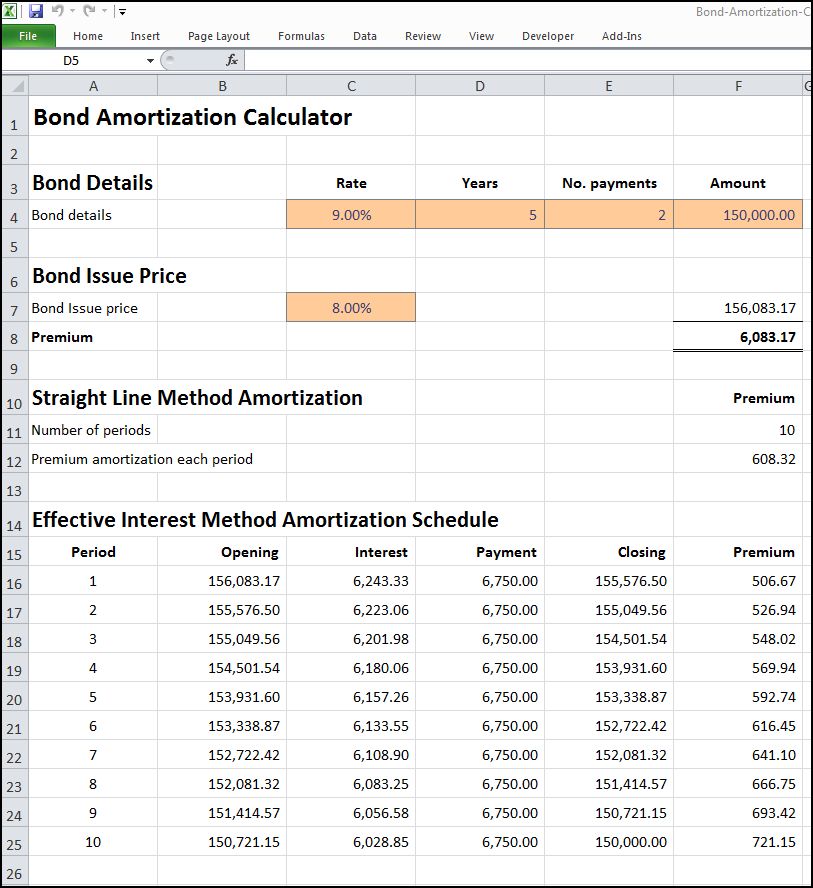
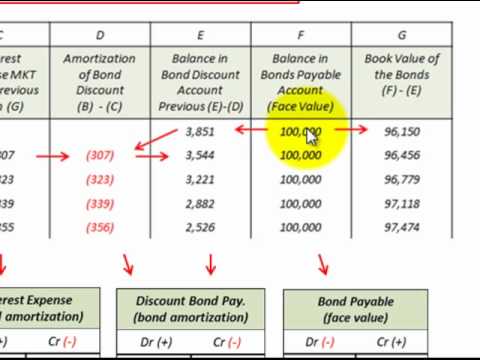
If you’re curious about how to calculate the amortized bond value, it’s actually pretty straightforward. The formula for calculating the amortized bond value is the present value of the future payments plus the present value of the face value. To calculate these values, you’ll need to know the annual interest rate, the number of payments, and the face value of the bond. The present value of the future payments is determined by subtracting the periodic payments from the face value and then dividing by the interest rate plus one. The present value of the face value is determined by dividing the face value by the interest rate plus one. Once you have these two values, you can add them together to get the amortized bond value. Calculating the amortized bond value can be a great way to determine the value of a bond before investing, as it gives you an idea of how much the bond will be worth in the future.
Exploring Different Types of Amortized Bonds
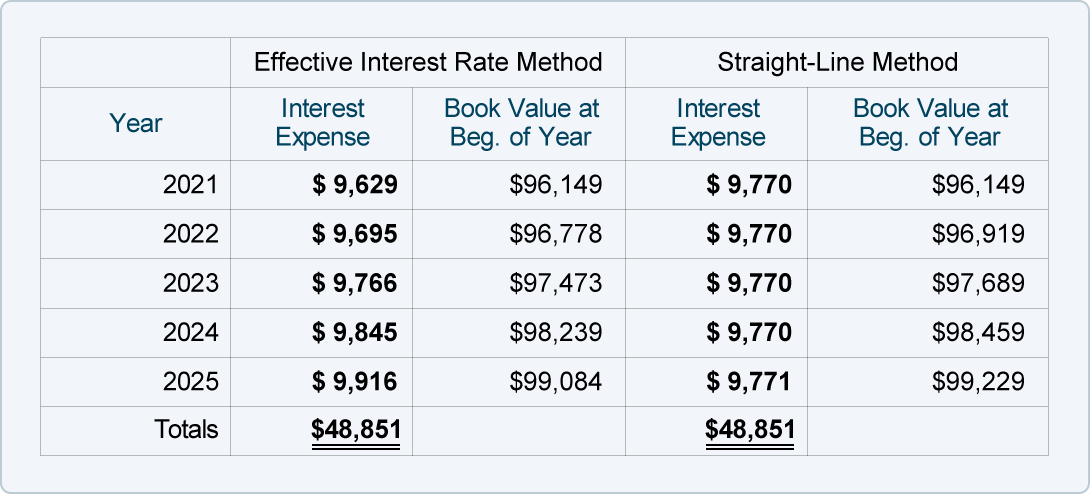
When it comes to investing in bonds, amortized bonds are one of the most popular choices. These bonds are typically issued by governments, corporations, and other organizations. They allow investors to receive regular payments of interest and principal over a set period of time. Amortized bonds can come in many different forms, such as fixed-rate bonds, floating-rate bonds, convertible bonds, and zero-coupon bonds. Fixed-rate bonds provide interest payments that remain the same over the life of the bond, while floating-rate bonds have interest payments that can fluctuate. Convertible bonds offer investors the option to convert their bonds into equity, and zero-coupon bonds provide no periodic interest payments and are sold at a discount. Investing in an amortized bond can provide investors with a steady income stream and a secure investment.
Risk Considerations with Amortized Bonds
When it comes to investing in amortized bonds, it’s important to consider the risks involved. Amortized bonds are essentially bonds that are issued with a set repayment schedule. The principal and interest payments are spread out over the term of the bond, meaning that the amount paid at each payment may vary. The risk with amortized bonds is that the payments may not cover the interest due, meaning that the bondholder may need to pay the difference out-of-pocket. Additionally, there is a risk that the issuer of the bond may default on the payments or that the market value of the bond may decline. It is important for investors to consider these risks when investing in amortized bonds, and to understand the terms and conditions of the bond before investing.