Amortization of Intangibles is an important concept in finance that can be difficult to understand. It is the process of spreading out the cost of intangible assets over their useful life. Intangible assets are assets that do not have a physical form and include intellectual property, copyrights, trademarks, and goodwill. By amortizing these costs, companies are able to spread out the expense of the intangible assets over a period of time, allowing them to more accurately reflect the company’s true financial performance. Understanding how amortization of intangibles works can help companies make better financial decisions.
What is Amortization of Intangibles?
Amortization of intangibles is a process where the value of an intangible asset is spread out over a period of time. This process is generally used for assets that have a long useful life, such as copyright, patent, or trademarks. It is similar to depreciation, except that it is used for intangible assets rather than physical assets. Amortization of intangibles is important for businesses to accurately calculate their financial statements, as it helps to accurately determine the value of the asset over time. It also helps to show the amount of income that a company is receiving over the life of the asset. Amortization of intangibles helps businesses to accurately determine the value of their intangible assets, and can provide important information when it comes to making decisions about investments and financing.
What are the Different Types of Intangible Assets?
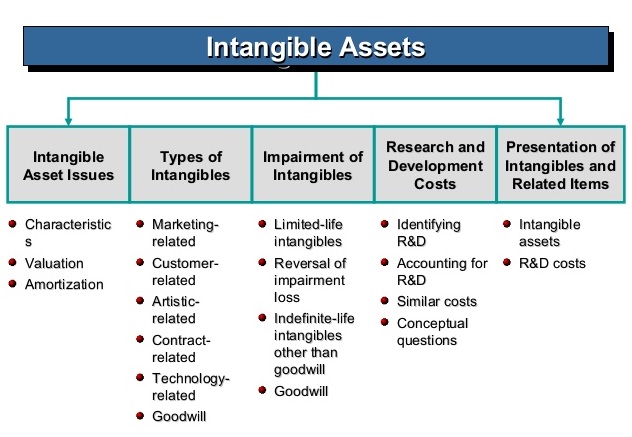
Intangible assets are non-physical assets that have value but can’t be seen or touched. They can include copyrights, trademarks, patents, goodwill, and intellectual property. Different types of intangible assets come with their own unique set of benefits and drawbacks. Copyrights are a form of protection for original works of art, literature, and music. Trademarks are symbols, words, or designs that identify a company’s products and services. Patents protect inventions and allow inventors to control the use of their invention to make a profit. Goodwill is the intangible value of a business based on its reputation and customer loyalty. Lastly, intellectual property are creations of the mind, such as inventions, literary and artistic works, symbols, and designs. Amortization of intangibles is the process of spreading the cost of an intangible asset over its useful life. This is done by taking a portion of the asset’s cost and allocating it to each accounting period. This allows businesses to spread out the cost of the asset to make it easier to manage. Amortization of intangibles helps companies maximize the value of their intangible assets and get the most out of their investments.
What is the Difference Between Amortization and Depreciation?

The difference between amortization and depreciation is an important concept to understand when it comes to accounting for intangible assets. Amortization is a method of spreading the cost of an intangible asset over its useful life and is commonly used for intangible assets such as software, patents, trademarks, and copyrights. This method of accounting is used to reduce the cost of the intangible asset in the company’s financial statements over a period of time, typically the asset’s useful life. Depreciation, on the other hand, is a method of accounting for the cost of tangible assets such as machinery and equipment. This method is used to reduce the value of the tangible asset over its useful life and is usually done on an annual basis. Both amortization and depreciation are methods used to reduce the value of assets over time, but they are used in different scenarios and are distinct from one another. Understanding the differences between amortization and depreciation is essential for any business to ensure the accuracy of their financial statements.
How does Amortization of Intangibles Affect Financial Statements?
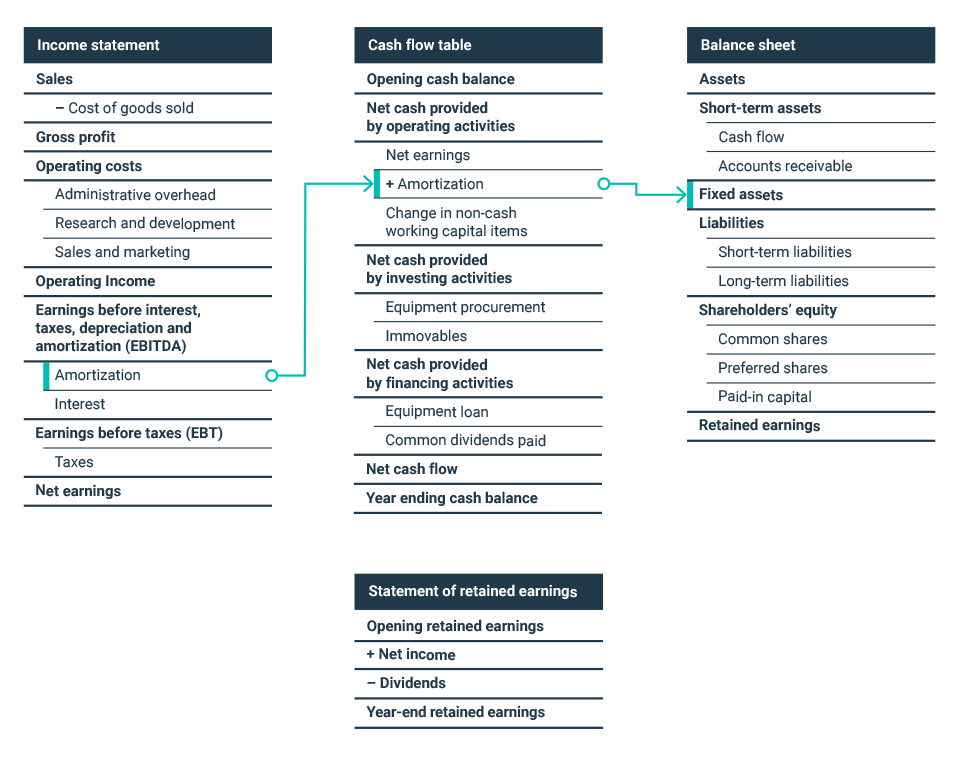
The amortization of intangibles can have a huge impact on the overall financial health of a company. While it’s not always immediately noticeable, amortization can drastically affect a company’s balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows. On the balance sheet, any intangible assets that have been amortized will be removed from the asset side and replaced with an amortization expense on the liabilities side. This is important because it ensures that the assets are not overvalued, which can lead to an inaccurate financial picture of the company. On the income statement, amortization of intangibles will be reflected as an expense, reducing the company’s overall profits. Finally, on the statement of cash flows, amortization will be reflected as a non-cash expense, meaning that it does not affect actual cash flows, but rather the overall financial picture of the company.
What are the Benefits of Amortizing Intangible Assets?

Amortizing intangible assets can be a great way to save money and maximize profits. By amortizing intangible assets, businesses can spread out the costs of carrying these assets over a period of time, rather than having to pay for them all at once. This allows businesses to use their cash flow for other investments instead of having to use it all to purchase these assets. Additionally, amortizing intangible assets can help businesses to better manage their tax liabilities, since the costs are spread out over a period of time, rather than having to pay for them all at once. This can help to reduce the amount of taxes businesses have to pay, which can lead to more money in their pockets. Amortizing intangible assets can be a great way to save money and maximize profits in the long run.