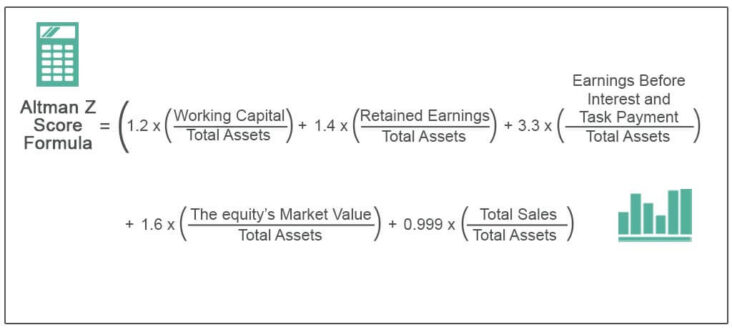
Altman Z-Score is a financial metric used to measure the health of a company’s financial position. It is based on a formula developed by Edward Altman in 1968 and uses information from a company’s financial statements to evaluate its risk of bankruptcy. The score is calculated from five factors that can be used to determine the probability of a company going into bankruptcy within two years. Understanding the Altman Z-Score is essential for investors to make sound financial decisions and assess the risk of investing in any particular company.
What Is Altman Z-Score and How Can It Help You Evaluate a Company’s Financial Health?
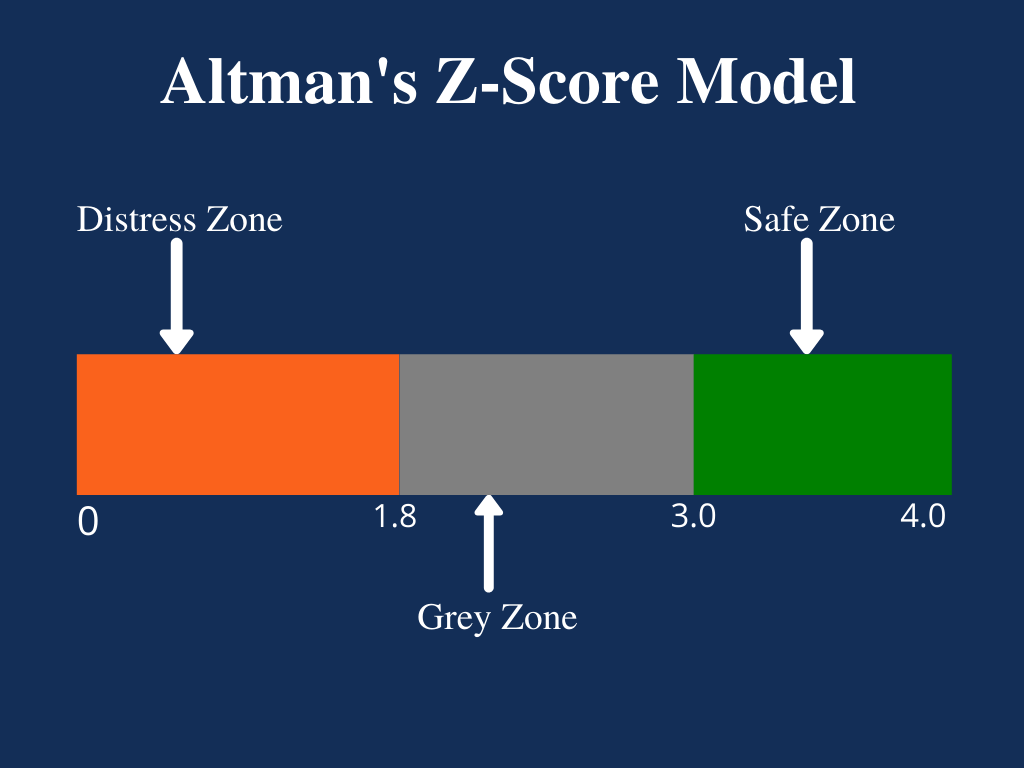
The Altman Z-Score is a great tool to help you evaluate a company’s financial health. It’s a single number, generated using multiple financial ratios, that provides an instant snapshot of a company’s ability to pay its creditors and stay afloat. By analyzing a company’s financial statements, the Altman Z-Score can help you identify potential red flags and make an informed decision about investing in a company. The higher the score, the more likely the company is to survive bankruptcy. If a firm has a score of 3 or higher, it’s considered to be in a safe zone. If the score is lower than 3, however, it could be a sign that the company is at risk of bankruptcy. Knowing the Altman Z-Score can help you make better decisions when it comes to investing in a company and help you protect your finances.
Factors to Consider When Analyzing a Company’s Altman Z-Score

When analyzing a company’s Altman Z-Score, there are several key factors that need to be taken into account. First, the company’s size and industry type should be considered. This is because different industries have different risk profiles, and larger companies typically have more resources and greater access to capital. Additionally, the operating cycle of the company should be taken into account. This is because companies that have very short operating cycles may have more volatile Z-Scores, while those with longer operating cycles may be more stable. Furthermore, the company’s financial leverage, profitability, and liquidity should also be considered. These all have an impact on the Altman Z-Score and can give a better indication of the company’s financial health. Finally, the accuracy of the data used should also be taken into account. This means making sure that the data is up to date and accurate, and that the company’s financial statements are properly audited. By considering all of these factors, investors can get a better understanding of a company’s financial health and make more informed investment decisions.
Understanding the Components of the Altman Z-Score Calculation
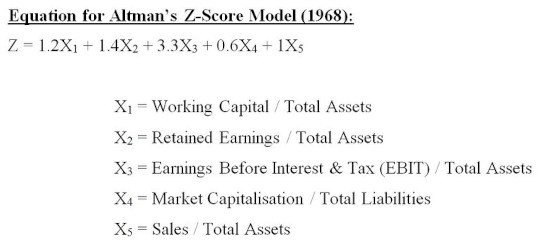
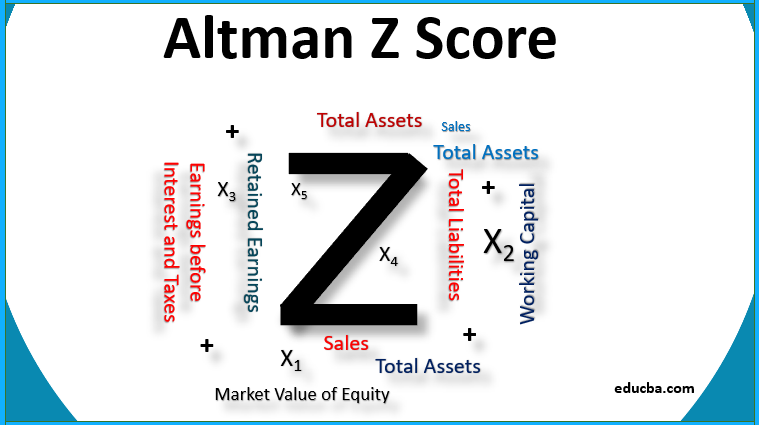
The Altman Z-Score is an incredibly useful tool for determining the financial health of a company. It’s made up of five distinct components that are used to calculate the score, which range from profitability to liquidity. To get a better understanding of how the Altman Z-Score works, let’s take a closer look at its components. The first component of the Altman Z-Score is Working Capital/Total Assets. This metric measures a company’s liquidity, and is calculated by subtracting Total Liabilities from Total Assets. The second component is Retained Earnings/Total Assets. This metric is used to measure a company’s profitability, and is calculated by dividing Retained Earnings by Total Assets. The third component is Earnings Before Interest & Tax/Total Assets. This metric is also used to measure a company’s profitability, and is calculated by dividing Earnings Before Interest & Tax by Total Assets. The fourth component is Market Value of Equity/Book Value of Total Liabilities. This metric measures a company’s overall financial strength, and is calculated by dividing Market Value of Equity by Book Value of Total Liabilities. Finally, the fifth and last component is Sales/Total Assets. This metric measures
Benefits of Using the Altman Z-Score to Analyze Companies

Using Altman Z-Score to analyze a company can be a great way to gain insight into its financial health. The Altman Z-Score is a simple yet powerful tool that can help investors understand the likelihood of a company entering bankruptcy. It’s a great way to measure a company’s financial strength and identify potential red flags that may indicate bankruptcy is on the horizon. It can also help investors spot companies that are undervalued and may be worth investing in. The score can be used to compare different firms and can provide a useful indication of a company’s financial stability. Furthermore, the score can be used to evaluate companies on a regular basis and can help investors keep an eye on the financial health of the companies they are considering investing in. Altman Z-Score is a great tool to have in a savvy investor’s toolkit.
How to Interpret an Altman Z-Score for Companies and Avoid Plagiarism
Interpreting an Altman Z-Score and avoiding plagiarism can be a tricky task. But it doesn’t have to be hard! By understanding what an Altman Z-Score is and what it measures, you can make sure you’re not making any mistakes when it comes to analyzing a company’s financial health. An Altman Z-Score is an equation used to measure the financial health of a company. It takes into account a company’s profitability, liquidity, and leverage to determine the probability of it going bankrupt within two years. It can help investors determine if a company is a safe investment or not. To interpret an Altman Z-Score, you need to look at the score and compare it to the industry standard. Scores above 2.99 are considered safe investments, while scores below 1.81 are considered high risk. Knowing this, you can assess the financial health of a company and make an informed decision on whether or not to invest. Make sure to do your research and understand what an Altman Z-Score means before making any decisions. That way, you can stay clear of plagiarism and make the best decisions for your investments.