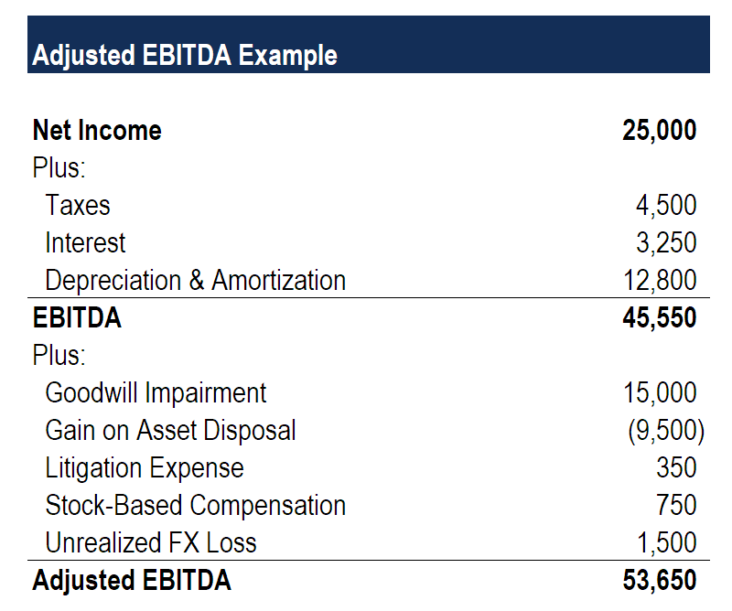
Adjusted EBITDA is a measure of financial performance that has become increasingly popular among investors and analysts. It is a useful tool for measuring a company’s profitability and financial strength and is often used to compare companies in the same industry. Adjusted EBITDA stands for Earnings Before Interest, Tax, Depreciation, and Amortization and excludes certain non-cash expenses, such as restructuring costs and stock-based compensation. In this article, we will discuss what Adjusted EBITDA is, why it is important, and how to calculate it.
Understanding the Definition of Adjusted EBITDA
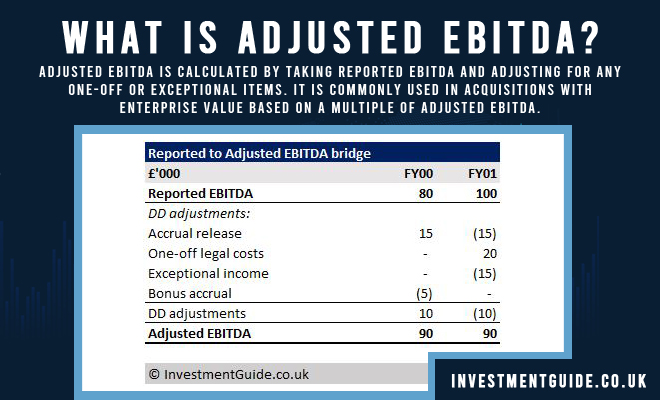
Adjusted EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Tax, Depreciation, and Amortization) is an important metric for measuring how profitable a company is. It is calculated by taking a company’s net income and adding back in any non-cash expenses such as depreciation, amortization, and other one-time costs. This gives a better understanding of a company’s actual cash flow and profitability. Knowing a company’s Adjusted EBITDA helps investors and analysts make more informed decisions when it comes to investing in a company. It is also useful for comparing companies in the same industry. By subtracting out non-cash items, you get a more accurate picture of a company’s performance, allowing you to make informed decisions. Adjusted EBITDA is a great tool for evaluating the health of a business, so understanding this metric can be invaluable to investors.
Calculating Adjusted EBITDA
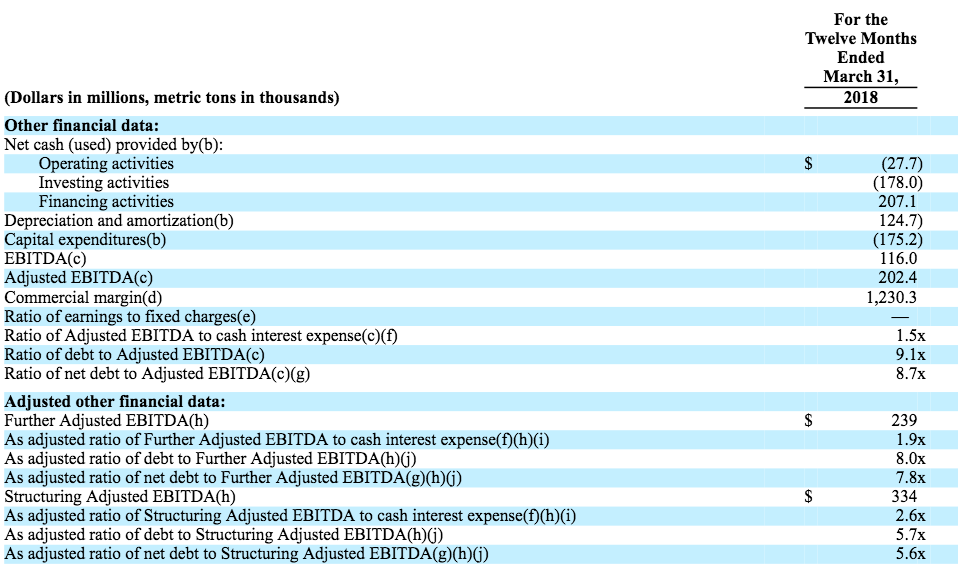
Calculating Adjusted EBITDA is a great way to measure a company’s overall financial health. It takes into account a company’s operating performance and helps you understand how much money the company is making. Adjusted EBITDA takes into account non-operating items such as taxes, depreciation, and amortization, as well as other non-cash items such as interest expense. This helps you get a more accurate picture of a company’s profitability. By subtracting these items from EBITDA, you get a truer indication of the overall health of a company. This measurement can be used to compare companies across different industries and make informed decisions about investments. It’s especially useful for investors looking to identify companies with strong financial performance.
Benefits of Using Adjusted EBITDA
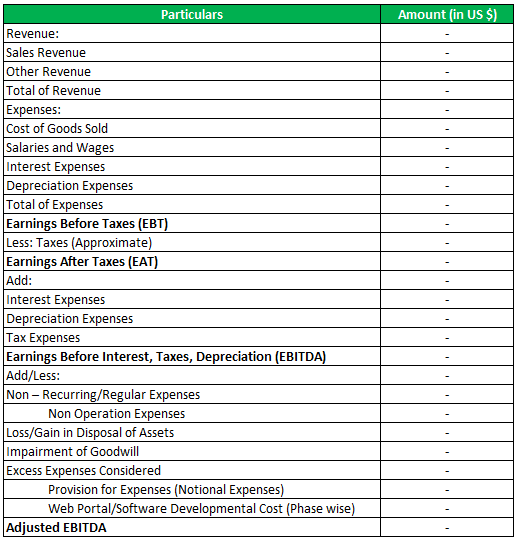
a blogAdjusted EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization) is an important financial metric that provides a measure of a company’s operational performance. It is a more comprehensive measure of profitability than net income because it excludes items such as non-operating income and expenses, non-recurring items, and capital investments. The use of Adjusted EBITDA provides a more accurate assessment of the company’s financial performance and allows investors to better compare companies with different capital structures, tax rates, and depreciation schedules.The benefits of using Adjusted EBITDA are clear. It provides a better understanding of a company’s performance by excluding non-recurring and non-operating items, allowing investors to more accurately compare the performance of companies with different capital structures, tax rates, and depreciation schedules. Additionally, it can be used to measure the performance of a company over time, as it is a more stable metric than net income, which can be heavily impacted by one-time items. Finally, Adjusted EBITDA is a good indicator of a company’s ability to generate cash flow and cover its debt obligations.
Disadvantages of Using Adjusted EBITDA
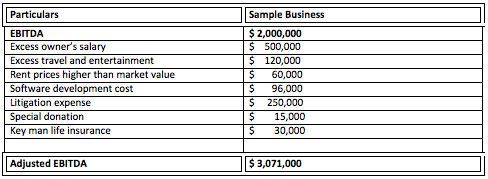
One of the main disadvantages of using Adjusted EBITDA is that it doesn’t always provide an accurate representation of a company’s financial health. While it’s a useful metric to measure profitability, it doesn’t always paint the complete picture. For example, Adjusted EBITDA doesn’t take into account any changes in the company’s cash flow or other financial obligations, such as debt payments. Additionally, some of the adjustments made when calculating Adjusted EBITDA, such as one-time expenses, can be misleading. These adjustments can make a company’s financials look better than they actually are, and can provide investors with a false sense of security. Finally, Adjusted EBITDA can be manipulated by management to present the company in a more favorable light. Therefore, it’s important to use caution when relying on Adjusted EBITDA as a metric for measuring profitability.
Tips for Accurately Calculating Adjusted EBITDA
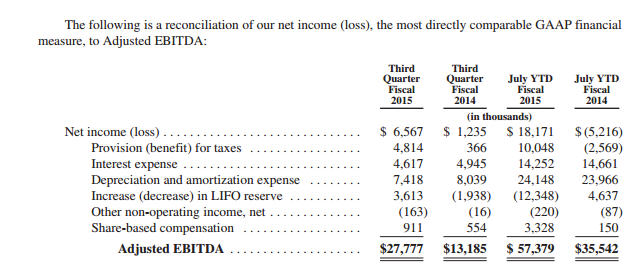
If you’re looking to accurately calculate Adjusted EBITDA, there are a few tips you should keep in mind. First, make sure you have a clear idea of what you want to measure. Adjustments to EBITDA should only be made when they’re necessary and relevant to the calculation. Additionally, be sure to use the right accounting principles when making adjustments. You should also remember to include any one-time costs or benefits that could affect the calculation. Finally, ensure accuracy by checking the results against past calculations and verifying that the numbers make sense. With these tips, you’ll be able to accurately calculate your Adjusted EBITDA and get a better understanding of your business performance.