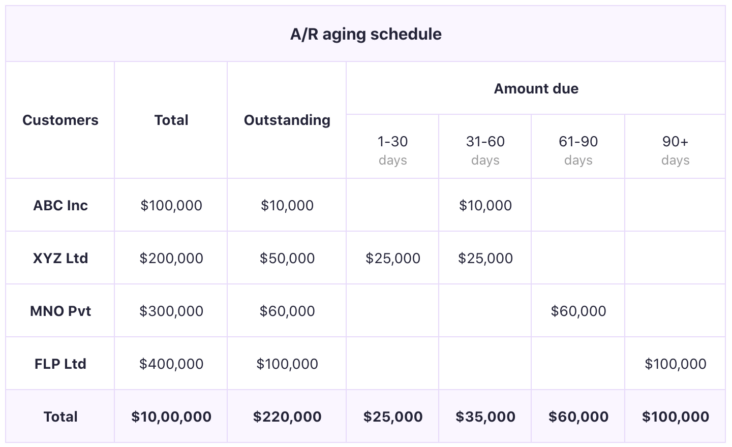
Accounts receivable aging is the process of categorizing invoices based on the length of time they have been outstanding. This information can be used to assess the creditworthiness of customers and to make decisions about extending credit or offering discounts for early payment.
While accounts receivable aging may seem like a dry and technical topic, it is actually an important tool for managing cash flow and reducing risk in your business. In this article, we will explore what accounts receivable aging is and how you can use it to your advantage.
What is Accounts Receivable Aging?
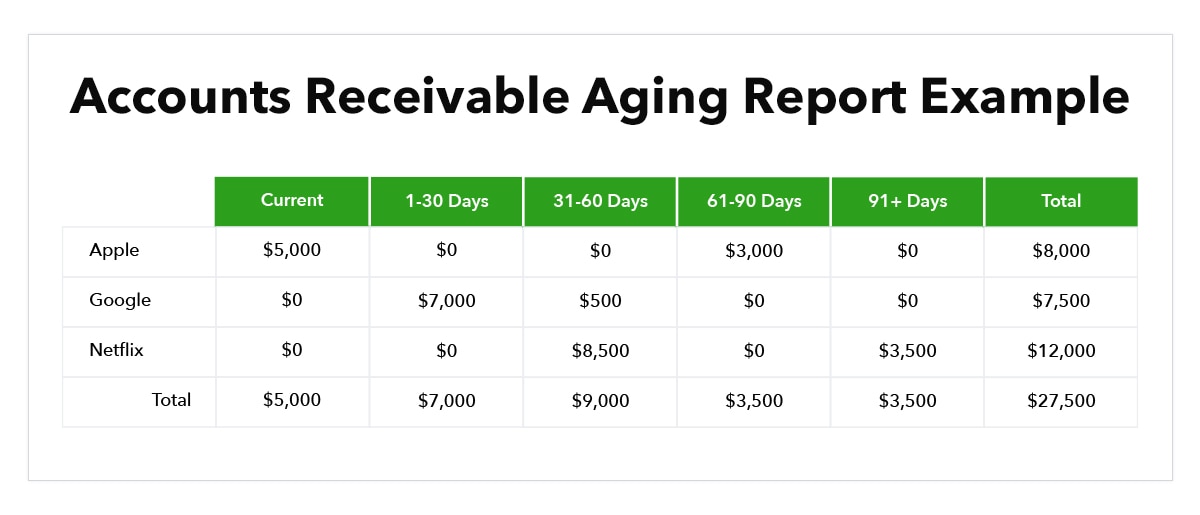
Accounts receivable aging is the process of categorizing and tracking outstanding invoices based on the length of time they have been outstanding. Accounts receivable aging can be used to identify invoices that are at risk of not being paid, and to prioritize collections efforts.
Most businesses will have some form of accounts receivable aging in place, as it is a valuable tool for managing cash flow and reducing bad debt. However, the specific details of how accounts receivable aging is carried out will vary from business to business.
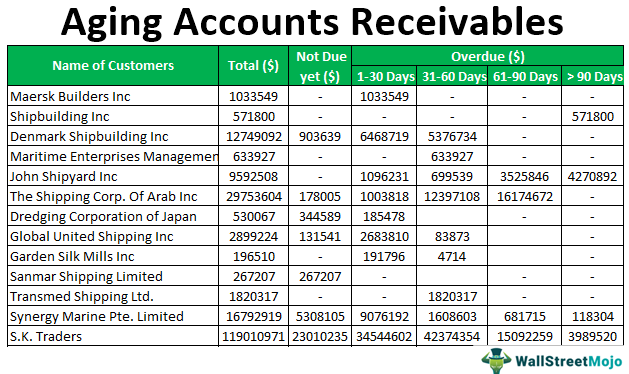
There are several different methods that can be used to categorize outstanding invoices in accounts receivable aging. The most common method is to divide invoices into 30-day buckets, although other businesses may use 15-day or 60-day buckets.
Once invoices are categorized by age, businesses can track the total amount owed in each bucket and compare it to previous periods. This can help to identify any trends in late payments, and to assess the effectiveness of collections efforts.
Accounts receivable aging can be a valuable tool for managing cash flow and reducing bad debt. However, it is important to ensure that accounts receivable aging is carried out in a way that is best suited to the specific needs of your business.
Pros and Cons of the Aging Method
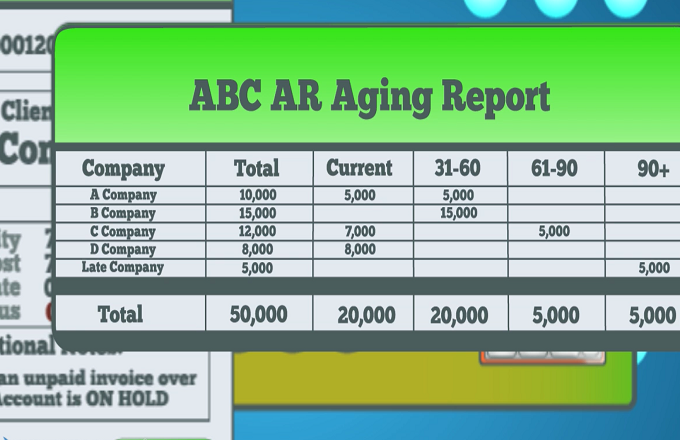
As with any financial decision, there are pros and cons to Accounts Receivable Aging. On the plus side, Accounts Receivable Aging can help you keep track of your money and who owes you what. This information can be very useful in negotiating payment terms with customers or taking legal action against those who don’t pay. Additionally, Accounts Receivable Aging can help you manage your cash flow by prioritizing which invoices to collect first.
On the downside, Accounts Receivable Aging can be time-consuming to set up and maintain. Additionally, it requires that you have detailed records of all your customer transactions. If you don’t have good records, Accounts Receivable Aging may not be accurate. Finally, some customers may not like that you’re using Accounts Receivable Aging to keep track of their payments – they may feel like it’s too intrusive or that you don’t trust them to pay on time.
How to Calculate Accounts Receivable Aging
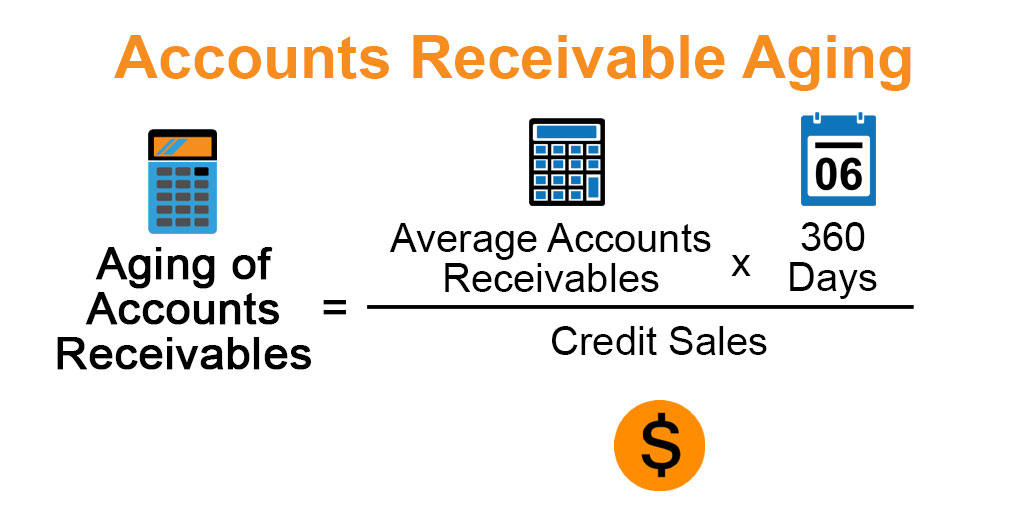
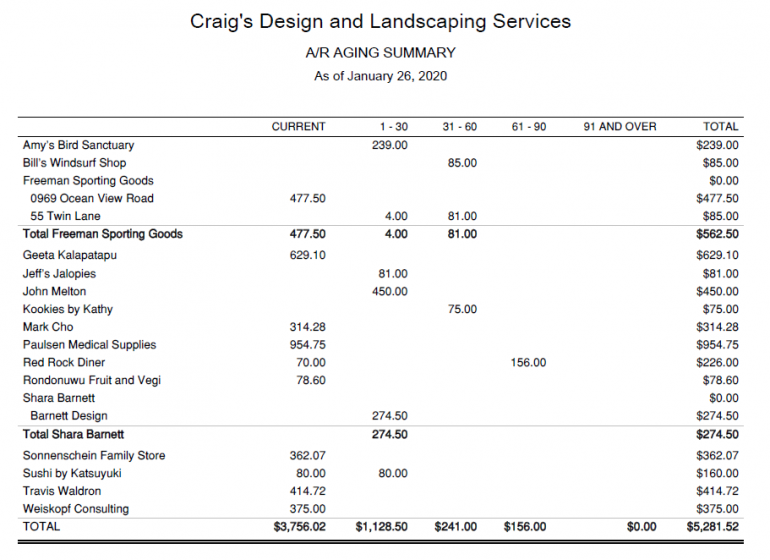
Assuming that you already have a list of your accounts receivable, you can calculate your accounts receivable aging by dividing your accounts receivable into buckets according to how many days past due each invoice is.
For example, you might have a bucket for 0-30 days past due, 31-60 days past due, 61-90 days past due, and 91+ days past due. To calculate the balance in each bucket, you would simply add up all of the invoices that fall into that category.
Accounts receivable aging can be a useful tool for managing your collections because it allows you to see which invoices are the most overdue and prioritize accordingly. It can also help you identify any trends in late payments so that you can take steps to prevent them in the future.
When to Implement the Aging Method
There are generally two different times when you would want to implement an accounts receivable aging system. The first is when you are starting a business. This will give you a way to keep track of customers who have not yet paid for their goods or services. The second time is when you are switching from another accounting method to this one. This will help you to keep track of customers who have not yet paid, as well as those who have already paid but whose payments have not yet been processed.
What Is Accounts Receivable Aging? – Accounts Receivable Aging Financial Definition
When a company sells products or services on credit, it records the sale as an accounts receivable. The customer then has a certain number of days to pay the invoice, after which time the account is considered past due.
Accounts receivable aging is the process of categorizing outstanding invoices by the number of days they are past due. This information is used to assess the risk of non-payment and to prioritize collections efforts.
Typically, accounts receivable are divided into four categories:
Current: invoices that are 0-30 days past due
Late: invoices that are 31-60 days past due
Very late: invoices that are 61-90 days past due
Collections: invoices that are more than 90 days past due
Accounts receivable aging can be done manually or with accounting software. The software will automatically generate aging reports that can be used to make decisions about collections and credit management.