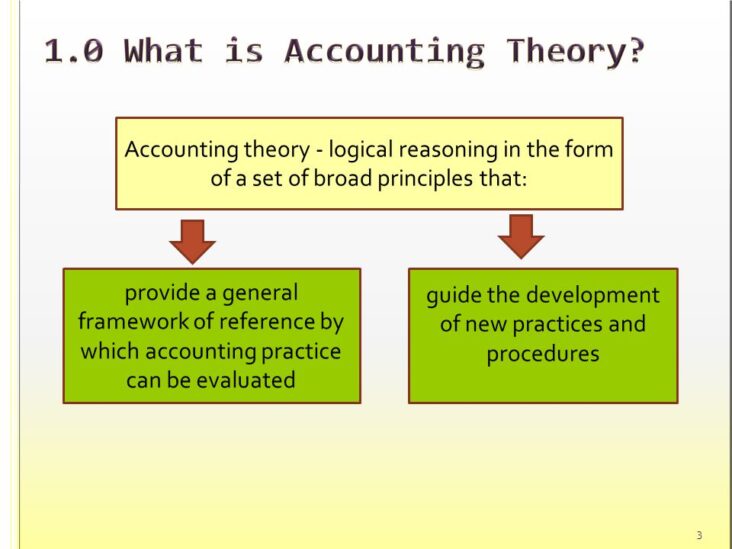
Accounting theory is a set of ideas that provides guidance to accountants. It includes principles, assumptions, and guidelines that accountants can use in their work.
The goal of accounting theory is to improve the practice of accounting. Theories can do this by providing guidance on how to choose between alternative accounting treatments, how to measure financial activity, or how to design accounting information systems.
-What is financial accounting theory?

Financial accounting theory is a set of ideas that explains how financial accounting works. It includes principles, assumptions, and rules that accountants use to prepare financial statements.
The goal of financial accounting theory is to provide a framework for understanding financial accounting. This framework can be used to make decisions about how to record transactions, what information to include in financial statements, and how to interpret financial statements.
Financial accounting theory is constantly evolving as new ideas are developed and new technologies are introduced. As a result, accountants must keep up with the latest theories in order to perform their jobs effectively.
-Types of accounting theory

There are four types of accounting theory: classical, neoclassical, behavioral, and managerial.
Classical accounting theory is the foundation of modern financial accounting. It was developed in the early 20th century and is based on the work of Italian economist and sociologist Vilfredo Pareto. Classical accounting theory focuses on financial statements and their impact on decision-making.
Neoclassical accounting theory emerged in the mid-20th century as a reaction to classical theory. It challenges the assumptions of classical theory and instead emphasizes the role of human behavior in accounting. Neoclassical theorists believe that people are rational decision-makers who act in their own best interests.
Behavioral accounting theory emerged in the 1960s as a response to neoclassical theory. It challenges the assumption that people are rational decision-makers and instead focuses on cognitive biases and emotions that can impact decision-making. Behavioral theorists believe that accounting choices are often made based on subconscious biases rather than rational thought.
Managerial accounting theory is a more recent development that focuses on how managers use accounting information to make decisions. It emphasizes the role of accounting in planning and decision-making, rather than just financial reporting. Managerial accounting theory also takes into account the impact of human behavior on decision-making.
-How did accounting theory evolve?

Accounting theory is a set of ideas that provides a framework for understanding and analyzing financial information. It includes principles, concepts, and rules that accountants use to prepare financial statements and report on financial transactions.
The development of accounting theory can be traced back to the early days of accounting practice. At that time, there was no formal body of accounting knowledge, and accountants relied on their own experience and intuition to guide their work. As the accounting profession grew, practitioners began to share their ideas and experiences with each other, and the need for a more formalized body of accounting knowledge became apparent.
The first major step in the development of accounting theory was the publication of Luca Pacioli’s treatise “Summa de Arithmetica, Geometria, Proportioni et Proportionalita” in 1494. Pacioli’s work was the first to codify theDouble-Entry Bookkeeping System, which is still in use today. Pacioli’s treatise also introduced many of the basic concepts of modern accounting, such as debits and credits, journal entries, and ledgers.
In the centuries that followed, accounting theory continued to evolve as new ideas were introduced and new insights were gained into how businesses operate. The development of modern accounting principles in the early 20th century was a major milestone in the evolution of accounting theory. These principles provide a framework for financial reporting that is still used today.
More recently, behavioral
-What are the major concepts in accounting theory?
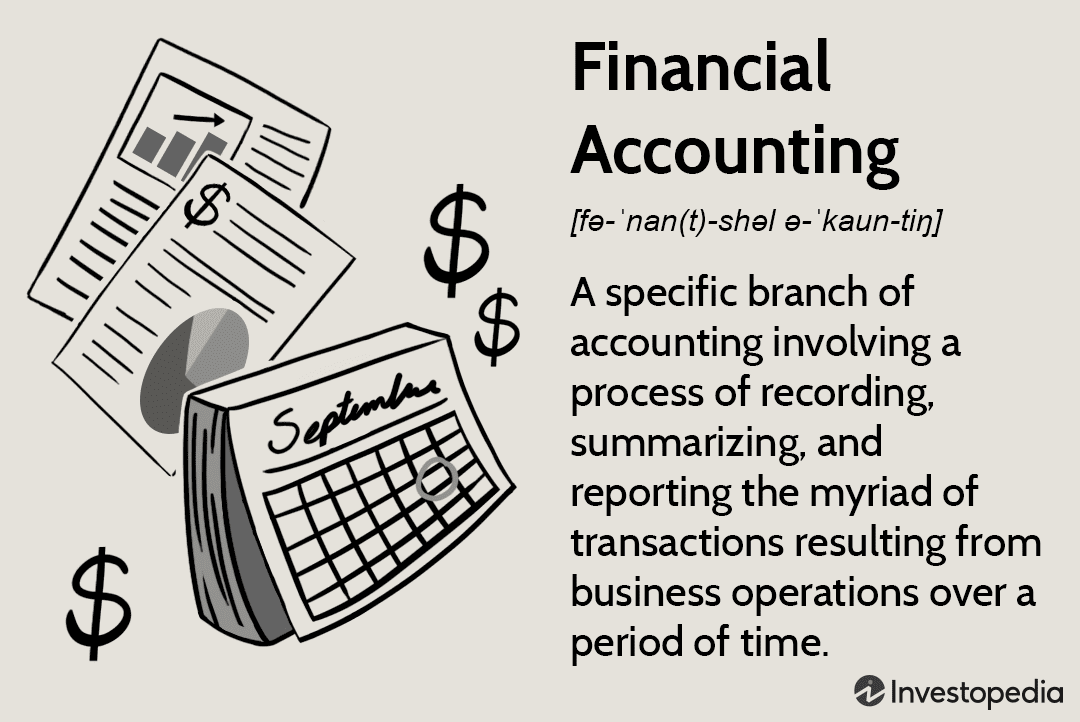
The basic concepts in accounting theory are financial statements, bookkeeping, and accrual basis accounting. Financial statements show a company’s financial position, performance, and cash flow. Bookkeeping is the process of recording, classifying, and summarizing financial transactions to provide information for decision-making. Accrual basis accounting recognizes economic events regardless of when cash is exchanged.
-Who’s the founder of accounting theory?

There are many different theories in accounting, but one of the most influential is the theory put forth by Luca Pacioli in 1494. Pacioli was an Italian mathematician and Franciscan friar who is credited with being the father of accounting and bookkeeping. He wrote a treatise on double-entry bookkeeping, which outlining the use of journal entries and ledgers to record financial transactions. This system is still in use today.
-Conclusion

While there is no one universally accepted accounting theory, there are several different schools of thought that provide useful frameworks for understanding and analyzing financial information. Accounting theory is important for both academic researchers and practicing accountants, as it helps to explain and predict financial behavior.
What Is Accounting Theory? – Accounting Theory Financial Definition
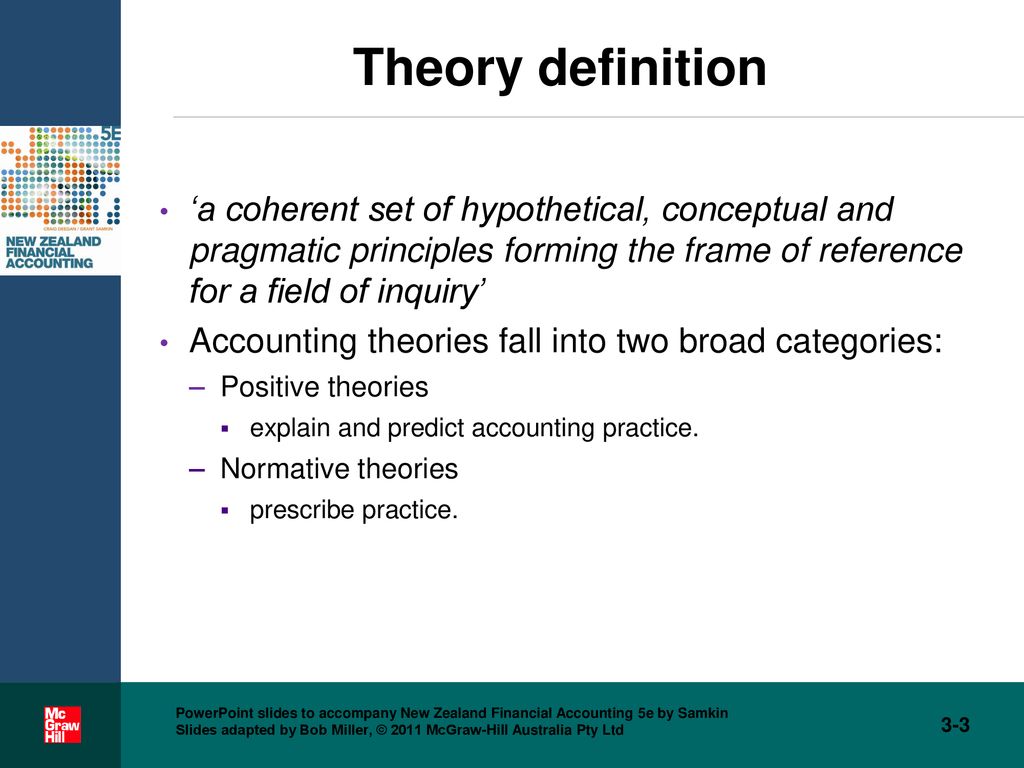
Accounting theory is a set of ideas that provides guidance to accountants when making financial decisions. The goal of accounting theory is to improve the quality of financial reporting.
There are three main types of accounting theory: positive accounting theory, normative accounting theory, and managerial accounting theory. Positive accounting theory is concerned with describing how people actually make financial decisions. Normative accounting theory is concerned with how people should make financial decisions. Managerial accounting theory is concerned with providing information that will help managers make better financial decisions.
Most accounting theories are based on one or more of the following assumptions:
* People are rational and act in their own best interests.
* People have limited information and must make decisions based on this limited information.
* People are risk-averse and prefer certainty to uncertainty.
* People behave predictably when faced with economic incentives.
These assumptions are not always accurate, but they provide a starting point for developing accounting theories.