An accounting information system (AIS) is a system of collecting, storing, and processing financial and accounting data that is used by decision makers.
An AIS is generally a computer-based system that processes transactions and converts them into information that can be used by managers, investors, tax authorities, and other stakeholders.
The main goal of an AIS is to provide accurate and timely financial information to its users. It accomplishes this by collecting data from various sources, processing it in accordance with pre-defined rules, and storing it in a central database. Financial statements and other reports can then be generated from the stored data.
Definition
An accounting information system (AIS) is a system that collects, stores, and processes data to produce financial and accounting information. An AIS typically consists of three components:
1. Data collection: Data is collected from various sources, including financial transactions, operational activities, and external data sources.
2. Data processing: The collected data is processed to produce financial and accounting information. This may involve various activities such as data entry, data validation, and data aggregation.
3. Reporting and decision-making: The processed information is presented in the form of reports and used for decision-making purposes.
Purpose
An accounting information system (AIS) is a system that captures and processes financial and accounting data and produces information useful to managers in making decisions.
The primary purpose of an AIS is to provide accurate and timely financial information to managers so that they can make informed decisions. An AIS also serves other purposes, such as helping managers keep track of the financial performance of the firm, providing information for tax preparation, and facilitating auditing.
While the primary purpose of an AIS is to provide accurate and timely financial information to managers, it also serves other important functions. For example, an AIS can help managers keep track of the financial performance of the firm, providing information for tax preparation, and facilitating auditing.
Structure

An accounting information system (AIS) is a system of records that an organization uses to collect, store, and process data related to its financial transactions. The system provides information that helps managers make decisions about the organization’s finances.
The AIS typically consists of three parts:
1. The source data: This is the raw data that comes into the system from financial transactions.
2. The processing system: This is the software that processes the data and produces financial reports.
3. The reports: These are the financial statements and other reports that managers use to make decisions about the organization’s finances.
Inputs
An accounting information system (AIS) is a system that collects, stores, and processes financial and accounting data to provide information that can be used by decision makers. An AIS can be used by businesses of all sizes, but is typically used by large organizations with complex business operations.
The purpose of an AIS is to provide accurate and timely financial information to those who need it. This information can be used to make strategic decisions about the direction of the business, or to make operational decisions about how to run the business on a day-to-day basis.
An AIS typically includes four main components:
1. Data collection – This component collects financial and accounting data from various sources within the organization. This data can come from transactions, such as sales or purchases, or from accounting records, such as ledgers or journals.
2. Data storage – This component stores the collected data in a central location. This storage can be either physical, such as in a filing cabinet, or electronic, such as in a computer database.
3. Data processing – This component processes the stored data to produce information that is useful for decision making. This processing can involve simple tasks, such as calculating totals, or more complex tasks, such as creating financial statements.
4. Information output – This component provides the processed information to those who need it. This output can be in the form of reports, graphs, or other visual representations of the data.
Outputs
An accounting information system (AIS) is a system that collects, stores, and processes financial and accounting data. The three main components of an AIS are the general ledger, accounts receivable, and accounts payable. The general ledger is a record of all the financial transactions that have taken place within a company. Accounts receivable is a record of all the money that is owed to a company by its customers. Accounts payable is a record of all the money that a company owes to its suppliers.
An accounting information system can either be manual or computerized. A manual accounting information system requires that all the data be entered into the system by hand. This can be a time-consuming and error-prone process. A computerized accounting information system automates many of the tasks involved in maintaining an accurate financial record. This includes tasks such as data entry, data processing, and report generation.
The benefits of using an accounting information system include increased accuracy, efficiency, and flexibility. An accounting information system can help managers make better decisions by providing them with timely and accurate financial information. It can also help businesses save money by reducing the need for manual data entry and processing.
System Features and Attributes
An accounting information system (AIS) is a structured system that collects, processes, stores, and reports financial and accounting data. The system is used to support financial planning and decision making by providing timely, accurate, and relevant information.
The main features of an accounting information system are:
1. Data collection: The system should be able to collect data from various sources, such as financial statements, transactions, and tax returns.
2. Data processing: The system should be able to process the data collected, such as calculating ratios and trends.
3. Data storage: The system should be able to store the processed data in a secure location.
4. Data reporting: The system should be able to generate reports based on the stored data. These reports can be used by managers to make informed decisions.
What Is Accounting Information System (AIS)? – Accounting Information System (AIS) Financial Definition
An accounting information system (AIS) is a system that collects and processes data and produces financial information. The purpose of an AIS is to provide timely, accurate, and relevant financial information to users who make decisions about the allocation of resources.
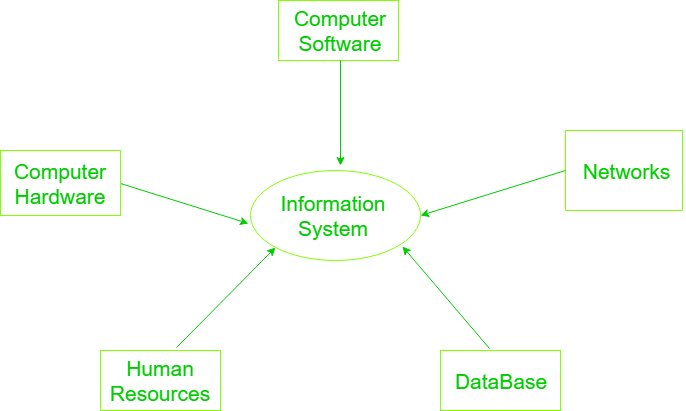
Accounting information systems are used in all types of businesses, from small mom-and-pop shops to large multinational corporations. An AIS typically includes a database, software applications, and hardware components. The database stores transactions and other financial data. Software applications process the data and generate reports. Hardware components include the computers and other equipment used to run the system.
Users of accounting information systems include managers, investors, creditors, and regulators. Managers use accounting information to make decisions about production, marketing, and other operational activities. Investors use accounting information to make decisions about buying, selling, or holding securities. Creditors use accounting information to assess the creditworthiness of borrowers. Regulators use accounting information to enforce compliance with laws and regulations.
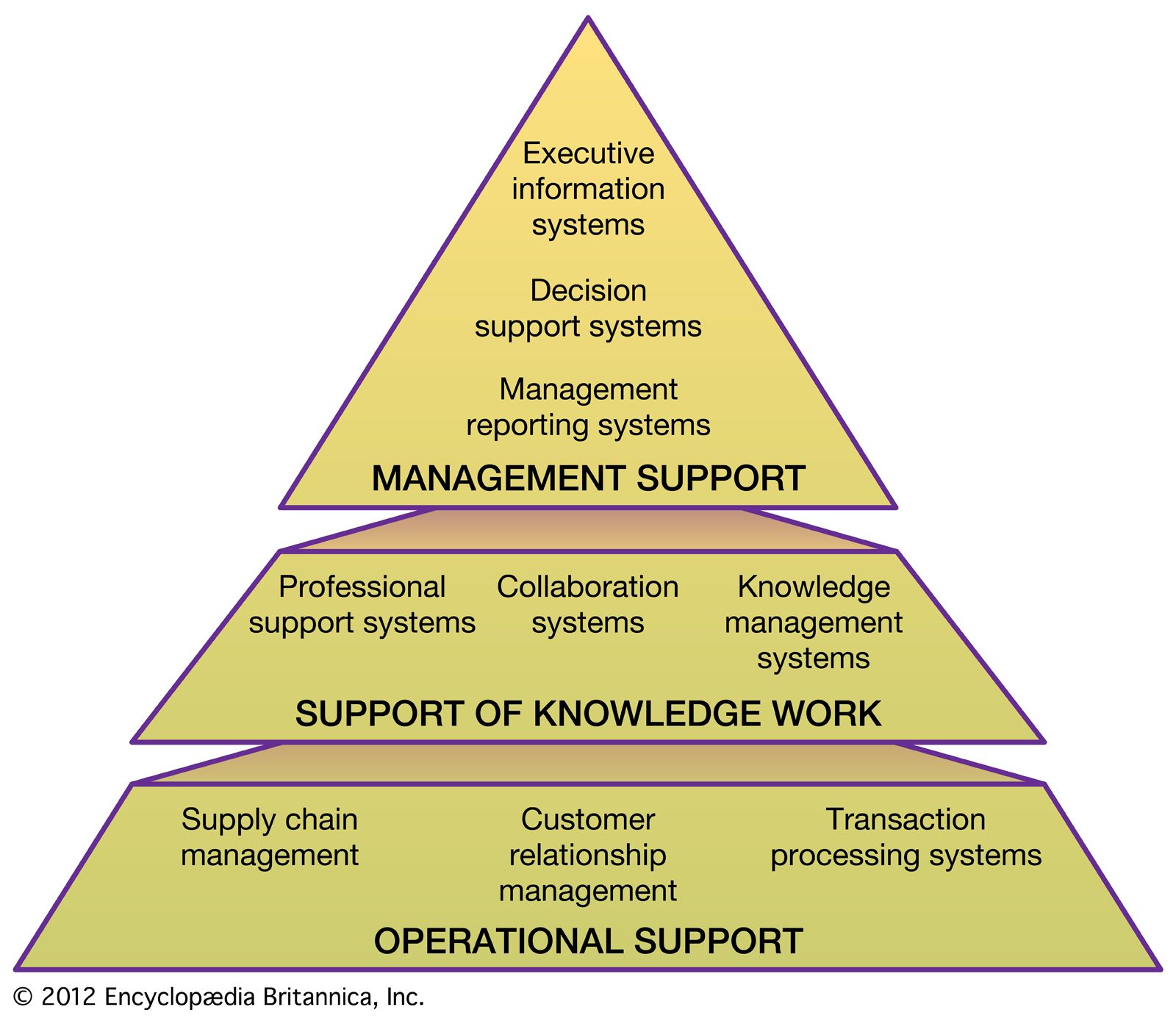
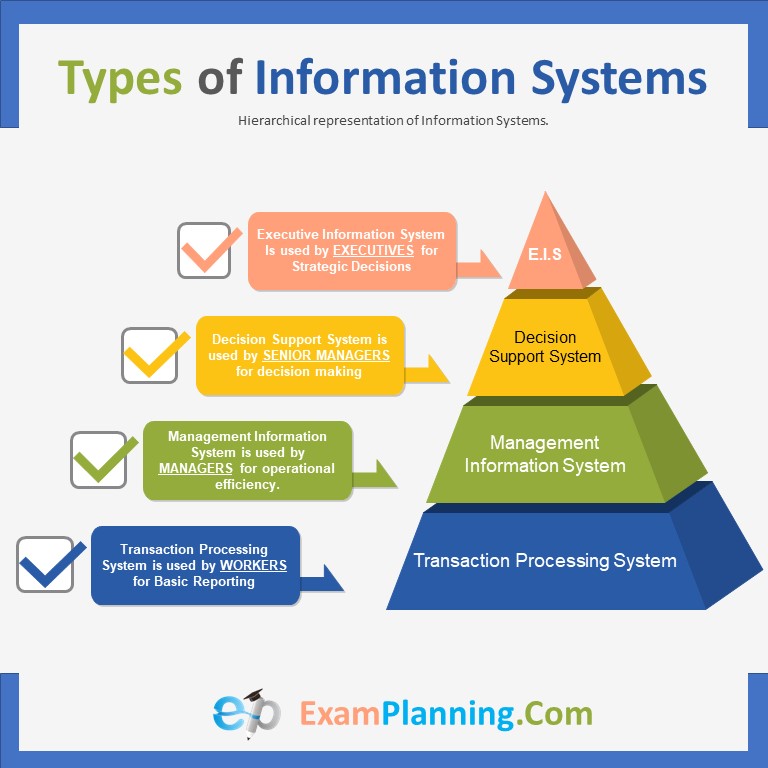
The three main types of accounting information systems are transaction-processing systems, management information systems, and decision-support systems. Transaction-processing systems record and process transactions. Management information systems provide managers with reports on organizational performance. Decision-support systems help users make decisions by providing them with access to relevant data and analytical tools.
Most organizations use a combination of all three types of systems. For example, a retail company might use a transaction-processing system to record sales transactions,