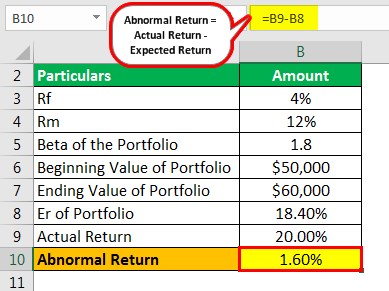
Abnormal return is the difference between the actual return of an investment and the expected return. The expected return is the normal return that an investor would expect to earn on an investment over a given period of time.
An abnormal return is either positive or negative, and it can be caused by a variety of factors. Some common causes include news announcements, earnings releases, and changes in analyst ratings.
In this article, we will take a deeper look at what abnormal return is and how it can impact your investments. We will also discuss some strategies you can use to maximize your returns while minimizing your risks.
What is Abnormal Return?

In finance, abnormal return is the difference between the expected return of an investment and the actual return of the investment. Abnormal returns can be either positive or negative.
Positive abnormal returns occur when an investment outperforms the market, while negative abnormal returns occur when an investment underperforms the market. Abnormal returns are often used to measure the performance of a security or a portfolio.
There are a number of factors that can cause abnormal returns, including economic news, changes in company fundamentals, and investor sentiment. While it is impossible to predict abnormal returns with 100% accuracy, there are a number of techniques that investors can use to try to forecast them.
Some common measures of abnormal return include the alpha and beta ratios. The alpha ratio measures the portion of an investment’s return that is attributable to factors other than the overall market movements, while the beta ratio measures the portion of an investment’s return that is attributable to market movements.
In conclusion, abnormal return is the difference between the expected return of an investment and the actual return of the investment. Abnormal returns can be either positive or negative and are often used to measure the performance of a security or a portfolio.
How to Calculate Abnormal Return

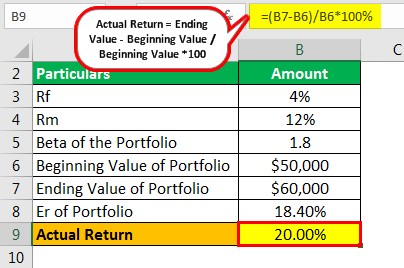
Assuming you have access to a Bloomberg Terminal, calculating abnormal returns is a relatively straightforward process. First, find the ticker symbol of the security in question and type “H” + the ticker symbol into the Bloomberg search bar. This will pull up the security’s historical prices. Next, calculate the stock’s return for each day using the following formula:
(Current Price – Previous Price) / Previous Price
Once you have calculated the return for each day, you can then find the abnormal return by subtracting the expected return from the actual return. The expected return can be calculated using a variety of methods, but the most common is to find the mean return of a group of similar securities over the same time period.
Calculating abnormal returns is a useful tool for investors because it allows them to identify stocks that may be under- or over-valued. However, it is important to remember that abnormal returns are not guaranteed and that past performance is not necessarily indicative of future results.
Financial Implications of Abnormal Return
Assuming that a security’s price has followed a random walk, any observed return on the security over a given period of time can be attributed to chance. However, if the security’s price deviates from what would be expected by chance alone, then the return is said to be abnormal.
There are a number of implications that arise from abnormal returns. Firstly, they can indicate that a security is under- or over-priced. Secondly, they can be used in statistical tests to determine whether a given return is statistically significant.
Lastly, and perhaps most importantly, abnormal returns can have a major impact on an investor’s bottom line. If an investor holds a security that experiences an abnormal return, then their investment will be worth more (or less) than it would have been if the return had been normal. This can have a big impact on an investor’s overall financial position.
What Is Abnormal Return? – Abnormal Return Financial Definition
An abnormal return is the return on an investment that is above or below the expected return. The expected return is the average return that investors expect to earn on an investment. Abnormal returns can be either positive or negative.
Positive abnormal returns occur when an investment earns a return that is higher than the expected return. Negative abnormal returns occur when an investment earns a return that is lower than the expected return.
Abnormal returns are often caused by factors such as changes in the economy, new information about a company, or changes in investor sentiment. They can also be caused by errors in estimating the expected return.
Abnormal returns can have a significant impact on investment decisions. They can cause investors to buy or sell an investment, and they can impact the price of an investment. Abnormal returns are an important consideration for both individual and institutional investors.