Aktiengesellschaft (AG) is a type of German corporation that is similar to the joint-stock companies found in other countries. AGs are subject to many of the same rules and regulations as other corporations and are governed by the Aktiengesetz (AktG) which was introduced in 1965. AGs are highly regulated and typically require a large minimum capital investment which makes them ideal for large enterprises. This article will provide an in-depth look at AGs and discuss the financial definition of Aktiengesellschaft as well as their advantages and disadvantages.
Introduction to Aktiengesellschaft (AG): Definition and Overview
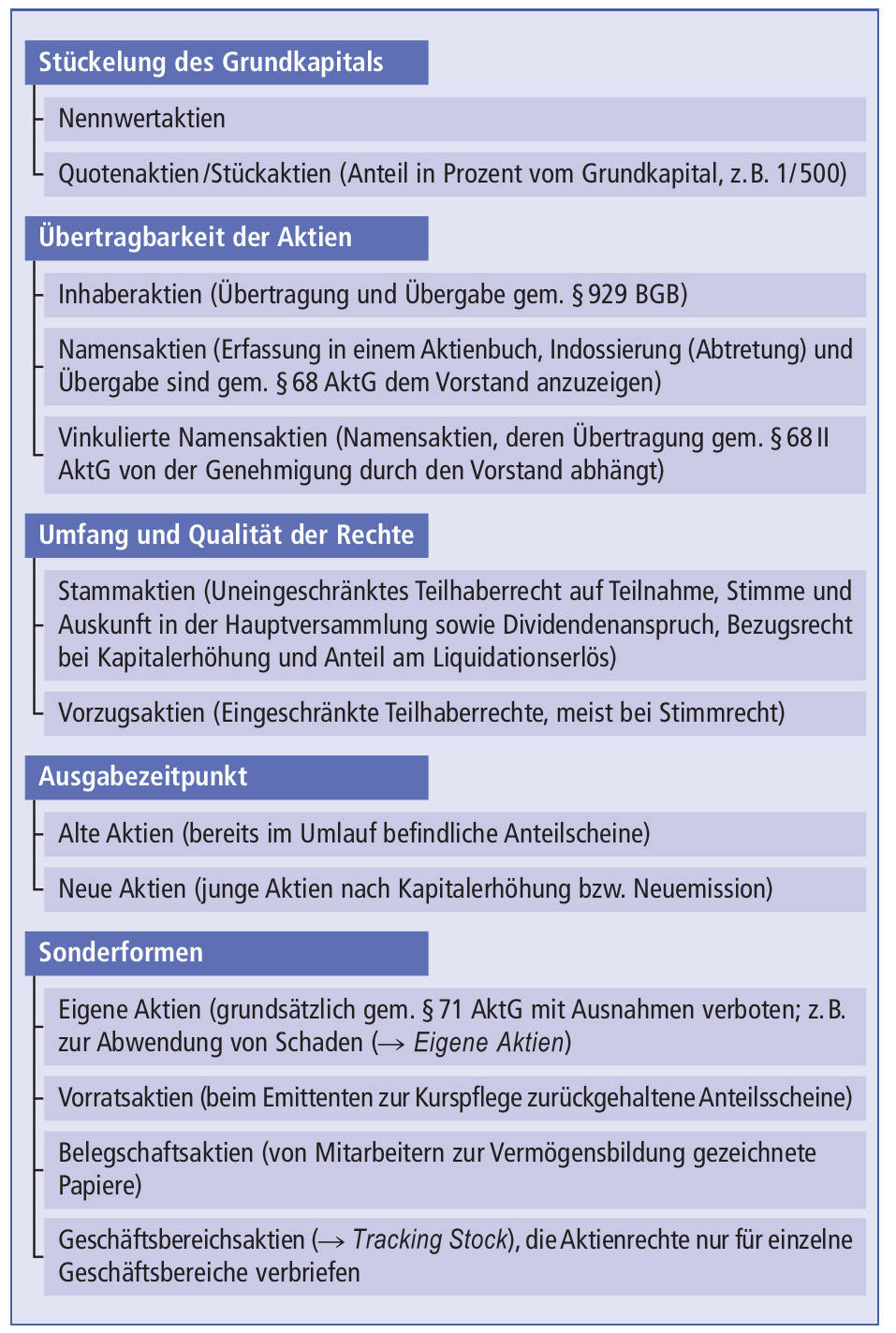
An Aktiengesellschaft, or AG, is a type of business entity that is popular in Germany and other European countries. This type of corporation is defined by its limited liability, meaning that shareholders are only liable for the amount of their investment, and not for any debts or other liabilities of the company. AGs typically have a supervisory board, which is made up of shareholders, and a management board, which is responsible for running the day-to-day operations. AGs are also publicly traded, meaning that their shares can be bought and sold on the stock market. AGs offer numerous advantages, including access to capital, low taxation, and ease of ownership. For these reasons, they remain a popular choice for business owners.
Benefits of Incorporating an Aktiengesellschaft (AG)

An Aktiengesellschaft (AG) is an incredibly beneficial way to incorporate a business. Incorporating an AG allows the business to become a legal entity, meaning it can own property and enter into contracts. This incorporation also separates the business and its owners from personal liability. As an AG, the business can also access capital by issuing stocks and shares and it can increase its creditworthiness. Additionally, AGs can have a flexible capital structure, and the owners of the business can easily transfer ownership and protect their assets. Ultimately, incorporating an Aktiengesellschaft (AG) is a great way to protect and grow your business, and it can provide a number of benefits that are unavailable to other forms of business.
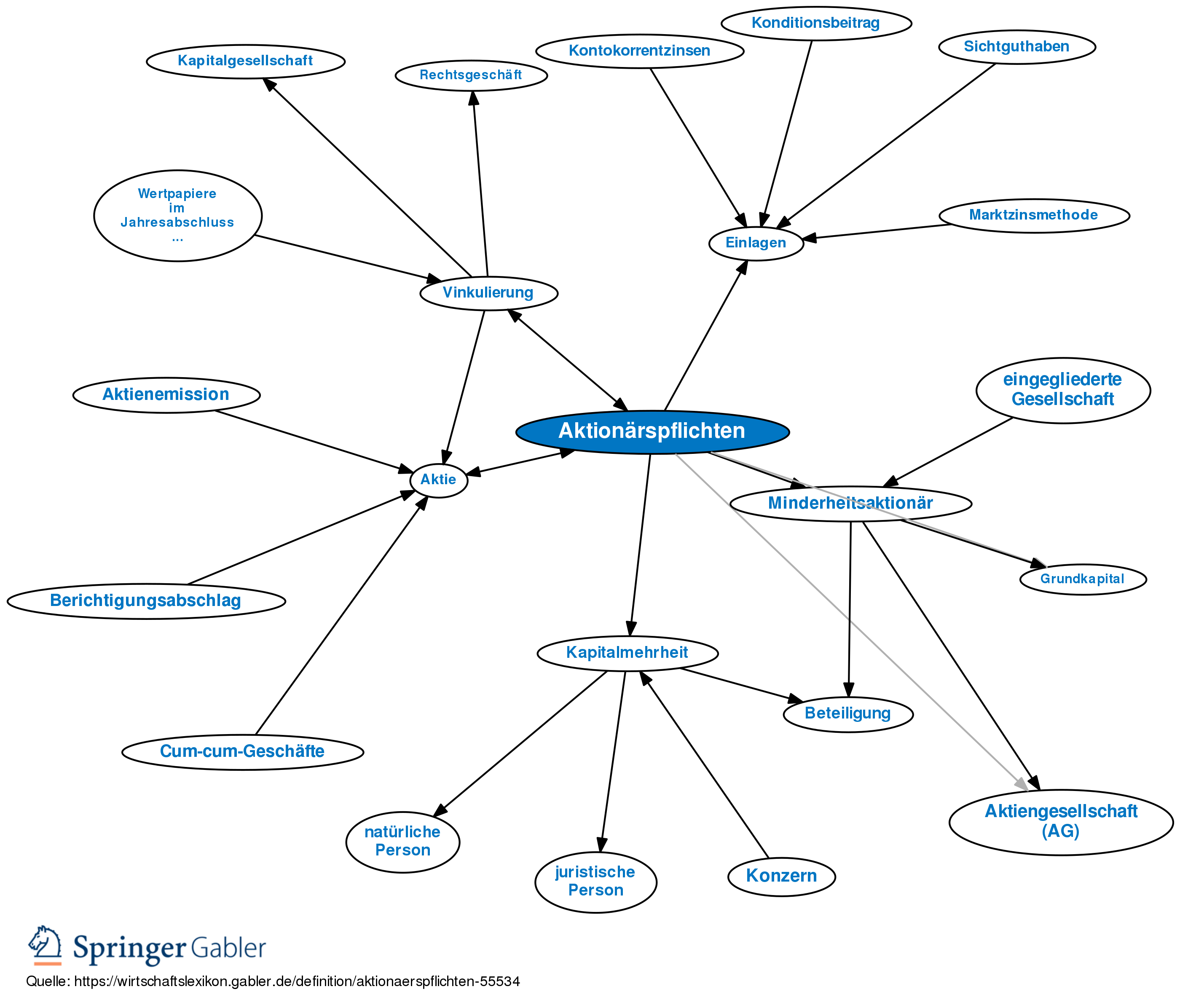
Aktiengesellschaft (AG) Shareholder Rights and Obligations
As an Aktiengesellschaft (AG) shareholder, you have certain rights and obligations that you should be aware of. Foremost, you have the right to vote at the AG’s annual general meeting, allowing you to have a say in the decisions that impact your investments. You also have the right to receive dividends on your shares, as determined by the AG’s board of directors. Additionally, you must protect the AG’s interests, including not disclosing confidential information, not acting against the AG’s interests, and not trading in AG securities. Finally, you must also abide by the AG’s regulations, such as its Articles of Association and shareholder rules. Being a shareholder of an AG is a big responsibility, but it can also be a rewarding investment.
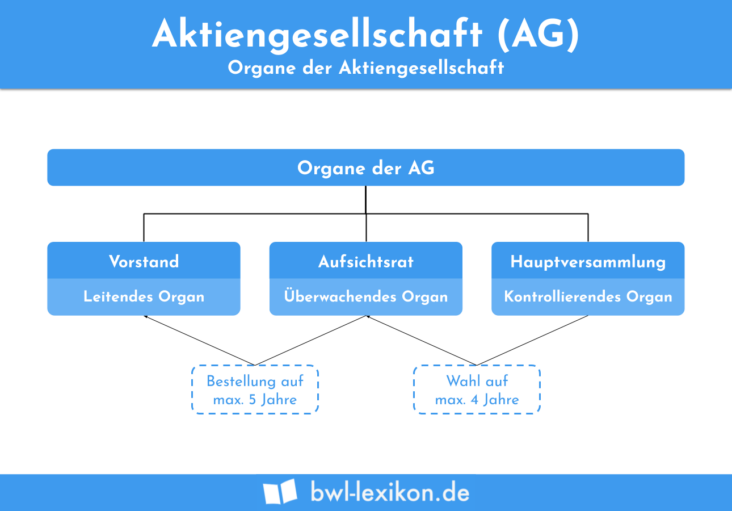
The Structure of an Aktiengesellschaft (AG)
An Aktiengesellschaft (AG) is a type of corporate structure that is popular in Germany and some other European countries. It is similar to the American corporation and is typically used by larger businesses. The AG is structured as a stock company, which means that the company is owned by shareholders who have limited liability. The AG is run by a board of directors and shareholders have the right to vote on key decisions. As with a corporation, the AG is treated as a separate legal entity from its owners and can own property, enter into contracts, and sue or be sued. The AG is also subject to certain regulations, such as the German Stock Corporation Act, and must file annual financial reports. With its many benefits and protections, an AG is an attractive option for businesses that are looking to expand their operations.
Common Use Cases for Aktiengesellschaft (AG) Companies
Aktiengesellschaft (AG) companies are some of the most popular business entities in Germany and other parts of Europe. They are used by a wide variety of organizations, from large multinationals to small start-ups looking to raise capital. AG companies have many advantages, including limited liability and the ability to access capital through the stock market. Common use cases for AG companies include manufacturing, technology, and financial services, as well as other industries. AG companies are also a great way for entrepreneurs to raise capital without having to make too many personal guarantees. The limited liability of AG companies can help protect founders from personal financial liability in the event of business failure. Furthermore, AG companies can provide the resources and capital needed to grow and expand the business. With the right team and strategy, AG companies can be the perfect vehicle for entrepreneurs to realize their dreams.