Have you ever wondered what an acceleration clause is? An acceleration clause is a provision in a contract that allows one party to the contract to accelerate the performance of the contract. In other words, it allows them to do something that they would not ordinarily be able to do under the terms of the contract.
An acceleration clause can be found in all sorts of contracts, from leases and loans to employment contracts. In this article, we will explore what an acceleration clause is, how it works, and some of the different types of acceleration clauses that you may come across.
Understanding an Acceleration Clause
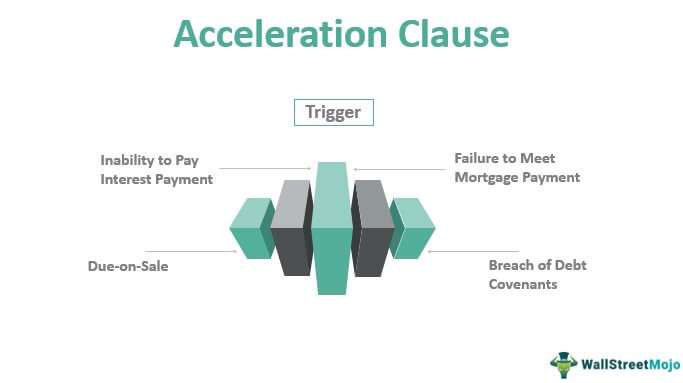
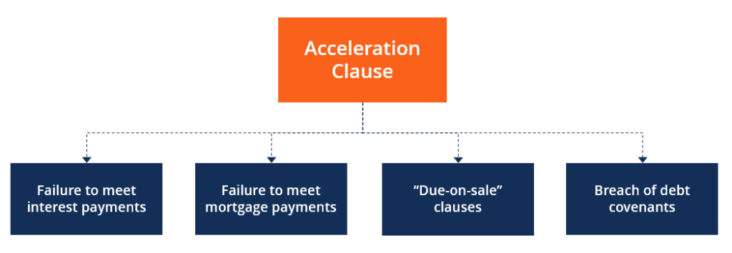
An acceleration clause is a term used in contracts that allows one party to speed up the payment schedule if the other party defaults. The clause typically states that if the debtor misses a payment, the entire balance becomes due and payable immediately.
Acceleration clauses are often found in loans, leases, and insurance policies. They protect the creditor by giving them the right to demand immediate payment if the debtor falls behind. This gives the creditor some security in knowing that they will eventually be paid, even if the debtor takes longer than expected to catch up on their payments.
acceleration clause can also be used as a way to motivate the debtor to keep up with their payments. If they know that missing a payment will result in the entire balance being due immediately, they may be more likely to stay current.
If you are considering agreeing to an acceleration clause, it is important to understand how it works and what your rights and obligations are under the contract. You should also make sure that you are comfortable with the consequences of defaulting before agreeing to anything.
When Is Acceleration Typically Used?
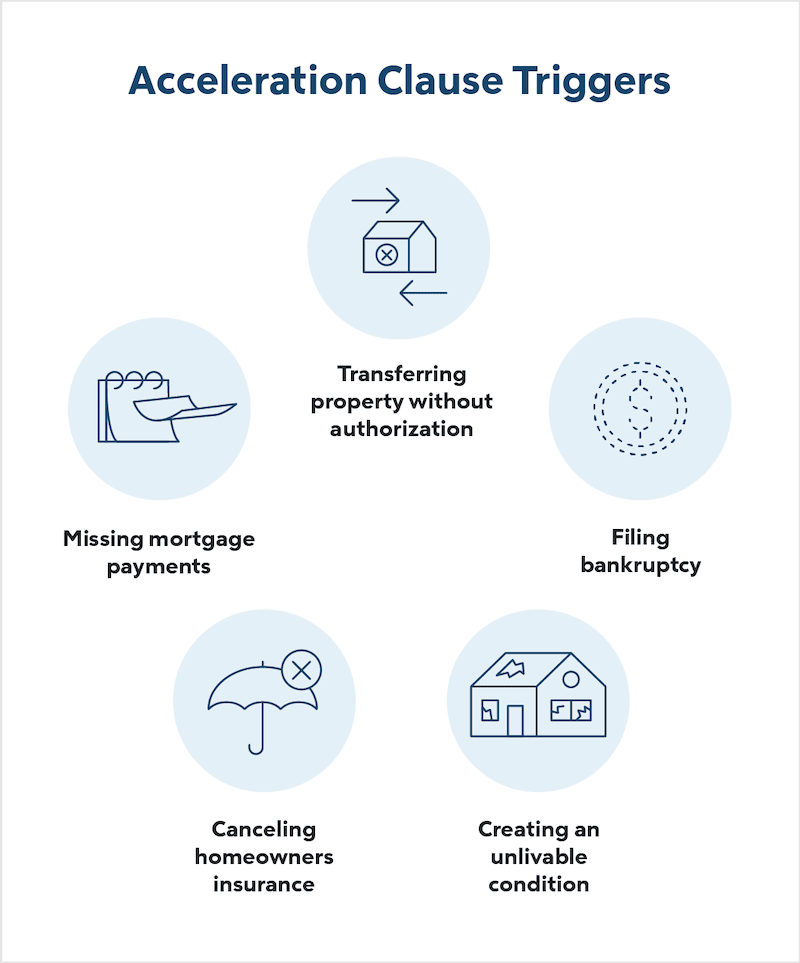
Acceleration is most commonly used in the business world when companies want to receive payments for services or products sooner than the original agreed-upon date. This could happen for a number of reasons, such as the company needing the money to cover unexpected expenses, or because the company is owed money by another party that is taking longer than expected to pay its own debts.
In some cases, acceleration can also be used as a way to encourage timely payments. For example, if a company is owed money by a customer who is habitually late on payments, the company may include an acceleration clause in their contract that states that any payments not made by the due date will be accelerated and the customer will be required to pay the full amount owed immediately. This type of clause can be effective in motivating customers to make their payments on time.
Common Issues with Acceleration Clauses
An acceleration clause is a provision in a loan or contract that allows the lender or other party to demand full payment of the outstanding balance under certain circumstances. The most common reason for invoking an acceleration clause is the borrower’s failure to make timely payments. Other grounds for acceleration include the borrower’s death, bankruptcy, or material breach of the terms of the agreement.
If an acceleration clause is invoked, the borrower typically has a limited time frame in which to pay off the entire balance of the loan or contract. If the borrower is unable to do so, the lender may take legal action to collect the debt.
While acceleration clauses are designed to protect the lender’s interests, they can also be disadvantageous to borrowers. In particular, borrowers who are facing financial difficulties may find it difficult or impossible to come up with the full amount due under an accelerated repayment schedule. As a result, borrowers should be aware of any acceleration clauses in their loan or contract agreements and try to negotiate more favorable terms if possible.
What Is Acceleration Clause? – Acceleration Clause Financial Definition

An acceleration clause is a clause in a contract that gives one party the right to require the other party to perform its obligations under the contract immediately, or at an earlier date than originally specified. The clause may also give the party the right to terminate the contract if the other party fails to perform its obligations.
An acceleration clause is typically used in loan agreements and leases. In a loan agreement, an acceleration clause may give the lender the right to accelerate the loan and demand repayment in full if the borrower misses a payment or defaults on the loan. In a lease, an acceleration clause may give the landlord the right to terminate the lease and evict the tenant if the tenant fails to pay rent or violates other terms of the lease.
Acceleration clauses are often used as a way to protect one party’s interests in a contract. For example, if a borrower defaults on a loan, an acceleration clause allows the lender to immediately demand repayment of the entire loan balance, rather than having to wait for future payments that may never be made. Similarly, if a tenant violates their lease, an acceleration clause allows the landlord to immediately terminate the lease and evict the tenant, rather than having to wait until the end of the lease term.
While acceleration clauses can be beneficial to one party, they can also be detrimental. For instance, if a borrower is only one month behind on their loan payments, an acceleration clause may allow the lender to demand immediate repayment of the entire loan balance, even