The term “absorption rate” is used in a number of different contexts, but it always refers to the speed at which something is taken in or used up. In business, absorption rate usually refers to the rate at which a company takes in revenue and then “absorbs” the costs associated with that revenue.
What Is Absorption Rate?
The absorption rate is the rate at which a particular substance is absorbed by another substance. For example, the absorption rate of a drug in the body is the rate at which the drug is absorbed by the body tissues. The term absorption rate is also used in finance, where it refers to the rate at which funds are used up or “absorbed” by an organization or project.
Definition of Absorption Rate
The absorption rate is the rate at which a drug is absorbed into the bloodstream. The absorption rate is affected by many factors, including the type of drug, the route of administration, and the individual’s physiology.
The absorption rate is a important consideration in pharmacokinetics, as it determines the concentration of the drug in the bloodstream and thus its efficacy.
Uses of Absorption Rate
The absorption rate is the speed at which a particular substance is absorbed by the body. The rate of absorption can be affected by many factors, including the type of substance, the amount of the substance, and the individual’s own physiology.
There are many different ways in which the absorption rate can be measured, and the results may vary depending on the method used. For example, when measuring the absorption of a drug from the gastrointestinal tract, the bioavailability may be used as a measure of absorption. This measures the amount of drug that actually reaches the bloodstream and is available for use by the body.
Other methods of measuring absorption rates include determining the concentration of a substance in blood or plasma over time, or measuring how quickly a substance is excreted in urine. The results of these tests can be affected by various factors, such as how much fluid is consumed, how recently food was eaten, and individual differences in metabolism.
Absorption rates are important to consider when taking any type of medication, as they can affect how well the drug works. For instance, if a drug has a low absorption rate, it may not be effective at treating a condition. On the other hand, if a drug has a high absorption rate, it may cause side effects such as nausea or vomiting.
Differences Between Absorption Rates

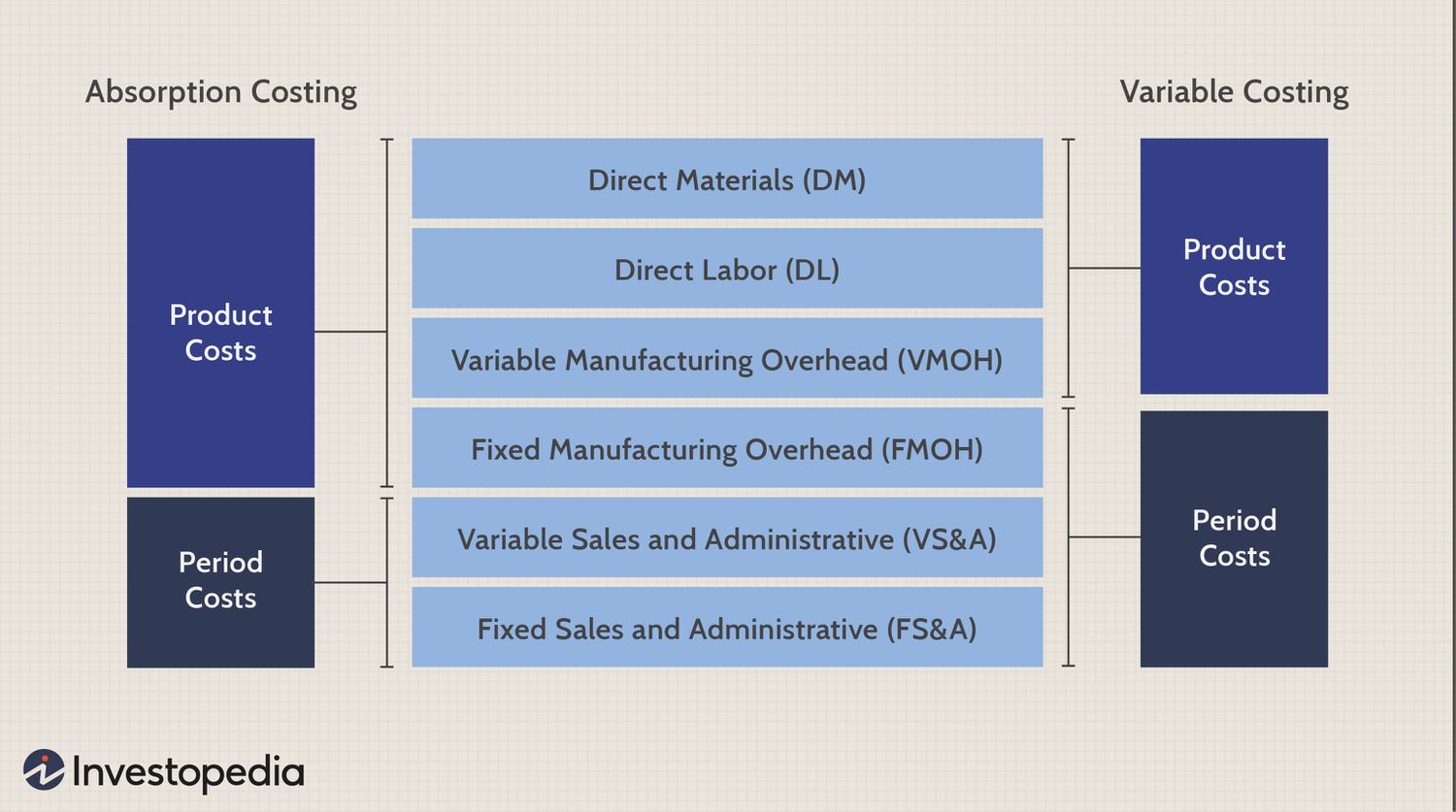
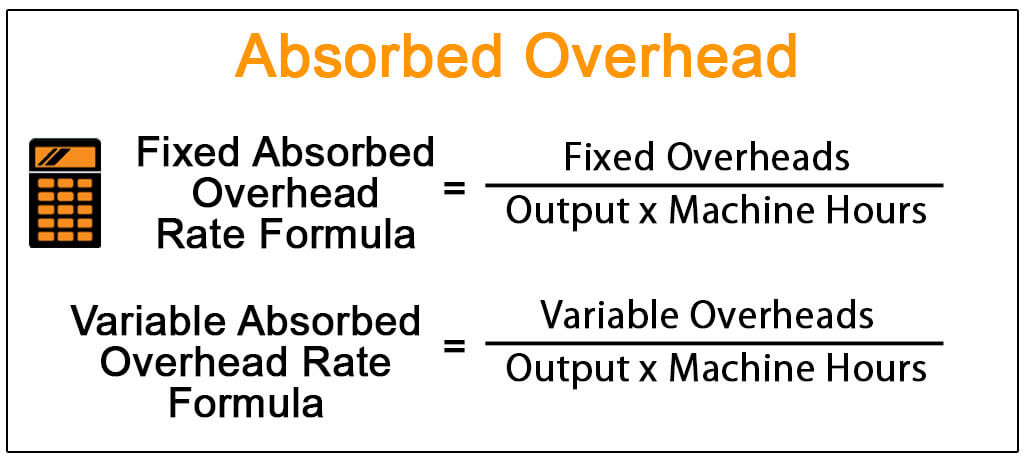
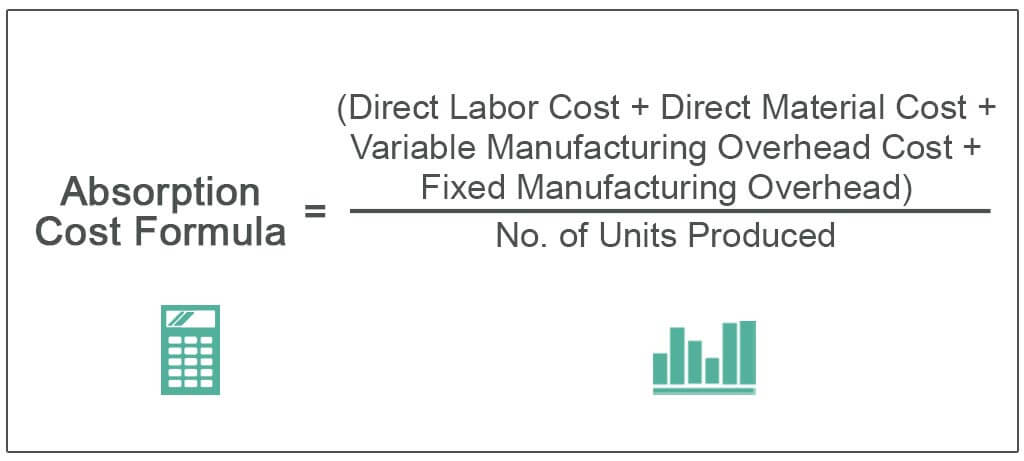
There are several different types of absorption rates that are used in financial analysis. The most common is the annual absorption rate, which is the percentage of a company’s sales that are absorbed by its fixed costs. This ratio is used to assess a company’s financial health and is a key metric in determining profitability.
Other types of absorption rates include the monthly absorption rate and the daily absorption rate. The monthly absorption rate is the percentage of a company’s sales that are absorbed by its fixed costs on a monthly basis. The daily absorption rate is the percentage of a company’s sales that are absorbed by its fixed costs on a daily basis.
Both the monthly and daily absorption rates are useful metrics for assessing a company’s financial health. However, they can also be useful for comparing different companies. For example, if Company A has a monthly absorption rate of 50% and Company B has a monthly absorption rate of 60%, this means that Company B is absorbing a higher percentage of its sales than Company A. This information can be used to make decisions about which company is more efficient and profitable.
How to Calculate an Absorption Rate

To calculate an absorption rate, divide the total number of units sold in a given period by the total number of units available for sale during that same period. For example, if 10 units are sold in a month and there are 50 units available for sale, the absorption rate would be 20 percent.
An absorption rate can be used to measure the rate at which a product is being sold or the rate at which a market is absorbing a new product. In the context of real estate, an absorption rate can be used to measure how quickly properties are being snapped up in a given market.
What Is Absorption Rate? – Absorption Rate Financial Definition

The absorption rate is the rate at which a financial asset is bought or sold in the market. The term is most commonly used in the context of bonds, where it is used to measure the rate at which a bond is being bought or sold in the market.
The absorption rate is calculated by dividing the number of bonds traded in a given period by the total number of bonds outstanding. The resulting percentage is then multiplied by 100 to get the absorption rate.
For example, if there are 100 bonds outstanding and 10 of them are traded in a given period, the absorption rate would be 10%.
The absorption rate can be used to gauge investor demand for a particular bond. A high absorption rate indicates strong demand for the bond, while a low absorption rate indicates weak demand.